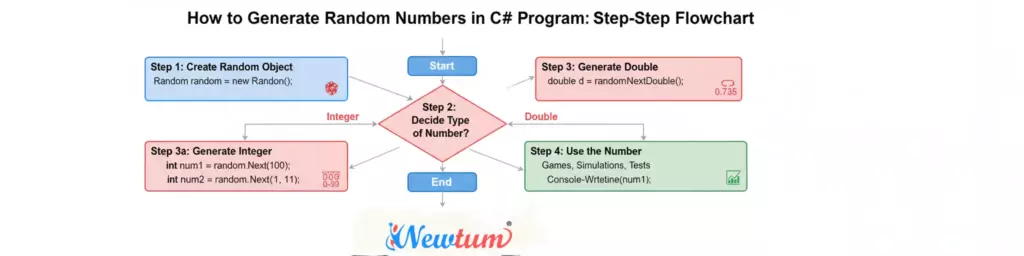
In C#, you can generate random numbers using the Random class. By creating an instance of Random and calling methods like Next(), you can quickly generate integers, doubles, or specific ranges of numbers.
Random numbers play a crucial role in programming, from building games and simulations to encrypting data and testing algorithms. If you’re learning C#, mastering its random number generator will make your projects more dynamic and realistic.
Key Takeaways
- Use Random Class →
Random rand = new Random(); - Generate Integers →
rand.Next(); - Set Range →
rand.Next(min, max); - Generate Doubles →
rand.NextDouble(); - Practical Use → Games, encryption, testing.
What is a Random Number Generator in C#?
In C#, random numbers are generated using the System.Random class. It is a pseudo-random generator, meaning the numbers are not truly random but sufficiently unpredictable for most applications like games, testing, and simulations.
Common methods of Random class:
Next()→ Generates a non-negative random integer.Next(min, max)→ Generates a random integer within a specific range.NextDouble()→ Generates a floating-point number between 0.0 and 1.0.NextBytes(byte[])→ Fills a byte array with random values.

How to Generate Random Integers in C#?
The simplest way is to call the Next() method without parameters.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
Console.WriteLine("Random Integer: " + rand.Next());
}
}
Sample Output:
Random Integer: 152934871How to Generate Random Numbers Within a Range?
You can pass two parameters to Next(min, max) to restrict values between a minimum and maximum number.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
int num = rand.Next(1, 101); // Random number between 1 and 100
Console.WriteLine("Random Number (1-100): " + num);
}
}
Sample Output:
Random Number (1-100): 47How to Generate Random Floating-Point Numbers in C#?
The NextDouble() method returns a double value between 0.0 and 1.0.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
double num = rand.NextDouble();
Console.WriteLine("Random Double: " + num);
}
}
Sample Output:
Random Double: 0.672315628345You can scale it up to a range, e.g. (rand.NextDouble() * 10) for values between 0.0 and 10.0.
Common Mistakes When Using Random in C#
- Creating multiple instances in loops
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Random rand = new Random(); // Wrong! Creates same seed Console.WriteLine(rand.Next()); }
This produces the same or very similar numbers because eachRandomobject is seeded with the system clock. ✅ Fix: Create a singleRandominstance and reuse it. - Not understanding pseudo-randomness
TheRandomclass is not suitable for cryptographic applications. UseSystem.Security.Cryptography.RandomNumberGeneratorinstead. - Seeding issues
Using the same seed always produces the same sequence. This is useful for testing but not for real randomness.
Comparison of Random Number Generation Methods in C#
| Method | Pros ✅ | Cons ❌ | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
Random.Next() | Simple to use, quick integer results | Limited to non-negative integers only | General apps, quick random integers |
Random.Next(min, max) | Generates numbers within a range | Still pseudo-random, not cryptographically secure | Games, simulations |
Random.NextDouble() | Produces doubles between 0.0–1.0 | Can’t directly set range beyond 1.0 | Probability, scaling random floats |
Random.NextBytes(byte[]) | Fills byte array with random data | Not commonly used, low flexibility | Data testing, encryption seeds |
RNGCryptoServiceProvider (now RandomNumberGenerator) | Cryptographically secure, unpredictable | Slower than Random, more complex code | Security, password generation, cryptography |
Real-Life Uses of C# Random Number Generator
Random numbers are more than just a coding exercise—they power real applications in gaming, testing, and finance. Let’s look at how companies and industries use them with practical C# examples.
🎮 Unity Game Engine – Random Enemy Movements
In games, random numbers are often used to decide where enemies spawn or how they move.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
int x = rand.Next(-10, 11); // Random X position
int y = rand.Next(-10, 11); // Random Y position
Console.WriteLine($"Enemy spawned at coordinates: ({x}, {y})");
}
}
Sample Output:
Enemy spawned at coordinates: (4, -7)In Unity, this randomness makes gameplay dynamic and unpredictable.
Microsoft .NET Testing Tools – Generating Mock Test Data
Test automation frameworks often need dummy data like IDs, ages, or phone numbers. Random numbers make this quick and reliable.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
int userId = rand.Next(1000, 9999);
int age = rand.Next(18, 60);
Console.WriteLine($"User ID: {userId}, Age: {age}");
}
}
Sample Output:
User ID: 4821, Age: 29Microsoft’s .NET testing libraries leverage random values to simulate real-world scenarios without relying on sensitive data.
Finance Apps – Simulating Stock Predictions
Finance applications use random numbers in Monte Carlo simulations to predict uncertain stock movements.
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
double basePrice = 100.0;
// Simulate random daily stock change (-5% to +5%)
double changePercent = (rand.NextDouble() * 10) - 5;
double newPrice = basePrice + (basePrice * changePercent / 100);
Console.WriteLine($"Predicted Stock Price: {newPrice:F2}");
}
}
Sample Output:
Predicted Stock Price: 103.45This randomness helps financial companies model risk and forecast possible outcomes.
Interview Topics: C# RNG
Diving into the world of C# programming, you’ll find a common curiosity about the Random Number Generator. This confidence trickster is pegged with questions you’re itching to crack. Here’s an exclusive list of queries you might not find elsewhere—those burning questions around the digital campfire of the internet:
- Why does C#
Randomgive the same number when I run my program?
Random seeds itself using the system clock. If your program runs multiple times within the same millisecond, the seed is identical → producing the same sequence.
Pro Tip (rarely shared):
Instead of relying on new Random() in loops or short runs, reuse a single instance of Random or use Random.Shared in .NET 6+ for thread-safe randomness.
// Recommended way (avoids same-seed problem)
int num = Random.Shared.Next(1, 100);2. Can I use C# Random for cryptography, like password generation?
Correct, Random is not secure. It’s predictable once the seed is known.
But in .NET 6+, you don’t need to manually use RNGCryptoServiceProvider. Instead, use the modern API:
using System.Security.Cryptography;
byte[] buffer = new byte[16];
RandomNumberGenerator.Fill(buffer);
Console.WriteLine(BitConverter.ToString(buffer));This gives cryptographically secure numbers—essential for passwords, tokens, and keys.
3. How do I generate a random decimal or float between two numbers in C#?
NextDouble() only returns values between 0.0 and 1.0. To scale it:
Random rand = new Random();
double min = 5.0, max = 10.0;
double result = min + (rand.NextDouble() * (max - min));
Console.WriteLine(result);This ensures a decimal in any custom range (not just 0–1).
3. Why does my random generator repeat numbers in a loop?
Yes, randomness can repeat—but many beginners confuse bad seeding with real randomness.
If you’re creating new Random() inside a loop, you’re actually resetting the generator with the same seed.
✅ Fix: Create one Random object outside the loop and reuse it:
Random rand = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine(rand.Next(1, 100));
}5. How do I generate unique random numbers in C# without repetition?
Instead of repeatedly checking duplicates, you can shuffle a range of numbers using LINQ or Fisher–Yates shuffle.
using System;
using System.Linq;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Random rand = new Random();
var numbers = Enumerable.Range(1, 10).OrderBy(x => rand.Next()).ToList();
Console.WriteLine(string.Join(", ", numbers));
}
}Output:
7, 2, 9, 1, 5, 8, 3, 10, 4, 6This way, you get unique random values without slow duplicate checks.
Our AI-powered csharp online compiler lets users instantly write, run, and test their code. With intelligent suggestions and error detection, coding has never been easier or more efficient. It’s perfect for learners and developers aiming for seamless development and quick feedback, making coding a breeze.
Get Free C# Coding cheatsheet 25 programs for beginners!
Conclusion
The ‘C# Random Number Generator’ empowers developers with essential skills to generate dynamic data effortlessly, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. Feel the excitement of creating randomised solutions! Start experimenting today. For more in-depth knowledge on C#, Java, Python, and more, visit Newtum.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.