Special operators in C include unique operators like the comma operator and the pointer-to-member operator that control expression evaluation and object member access.
The comma operator evaluates multiple expressions sequentially, while the pointer-to-member operator is used to access class or structure members via pointers.
As C and C++ are still widely used in system programming, embedded systems, compilers, and high-performance applications, understanding lesser-known special operators in C can improve code efficiency and readability.
Many developers overlook these operators, yet they are commonly used in low-level libraries and performance-critical software.
Key Takeaways of Special Operators in C
- Risk → Can reduce readability if overused
- Comma Operator (,) → Executes expressions left to right and returns the last value
- Pointer-to-Member Operator (. , ->)** → Accesses class or struct members via pointers
- Use Case → Compact expressions, callback handling, object-oriented C++ logic
What Are Special Operators in C?
Special operators in C are operators that perform non-traditional tasks such as expression sequencing, indirect memory access, and advanced referencing.
Unlike arithmetic or logical operators, special operators are designed to control how expressions are evaluated or how data members are accessed.
They are commonly used in:
- Low-level programming
- Performance-critical code
- Compiler design
- Embedded systems
Examples of special operators include:
- Comma operator
(,) sizeof- Pointer-related operators
- Pointer-to-member operators (primarily in C++)
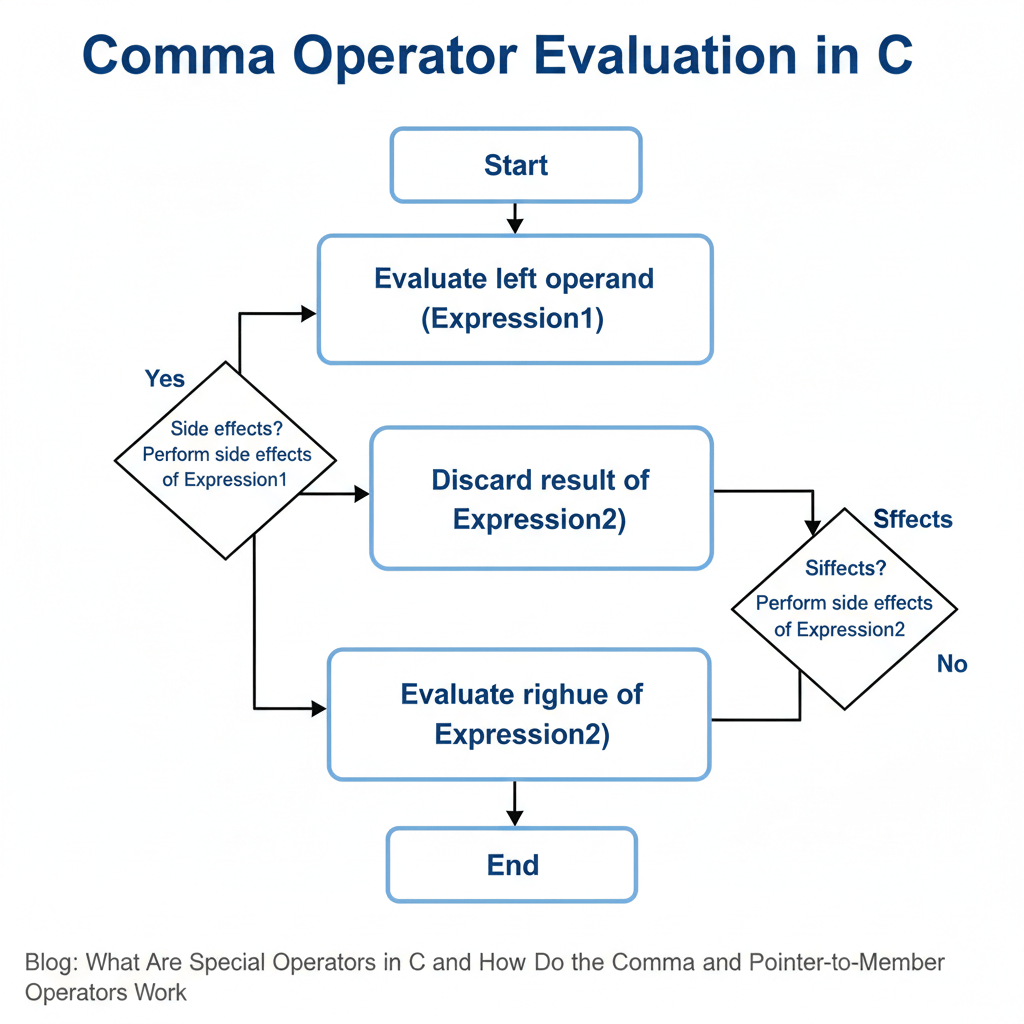
What Is the Comma Operator in C?
The comma operator allows multiple expressions to be evaluated from left to right, returning the value of the last expression.
This makes it useful in scenarios where multiple operations must occur in a single statement.
Syntax
expression1, expression2
✔ Example
int x; int a = (x = 5, x + 2);
✔ Output
7Explanation:
x = 5is evaluated firstx + 2is evaluated next- The final value returned is
7
When Should You Use the Comma Operator?
The comma operator should be used intentionally and sparingly, mainly when clarity or compactness is required.
✔ Common Use Cases
- In
forloops
for (int i = 0, j = 10; i < j; i++, j--)
- Macro definitions
- Compact variable initialization
- Sequential execution inside expressions
⚠️ Best Practice:
Avoid using the comma operator in complex expressions where readability suffers.
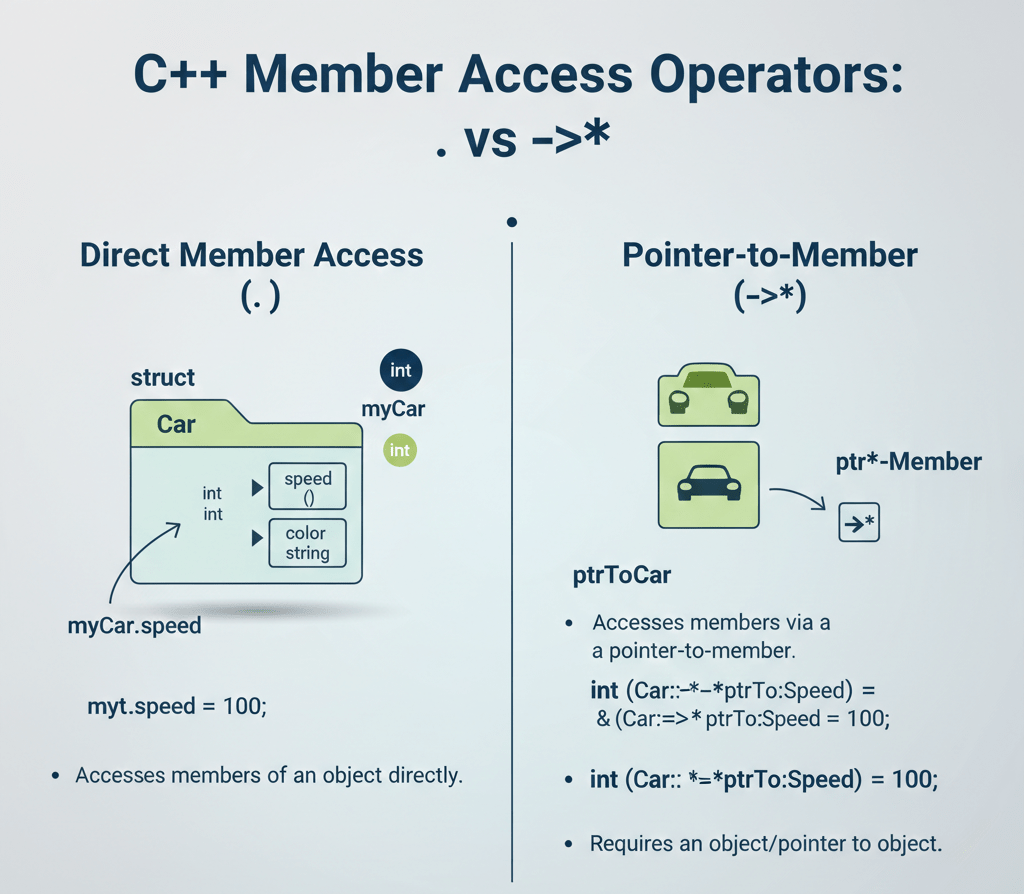
What Is the Pointer-to-Member Operator?
The pointer-to-member operator is used to access class or structure members through pointers, rather than direct object references.
This operator is primarily used in C++, not in pure C, and is valuable in dynamic object-oriented designs.
Syntax
object.*pointerToMember pointerToObject->*pointerToMember
How Does Pointer-to-Member Work in C++?
The pointer-to-member operator enables indirect access to class members, making it useful for:
- Callback mechanisms
- Event handling systems
- Function dispatch tables
- Framework and library development
Example
class Sample {
public:
int value;
};
int Sample::*ptr = &Sample::value;
Sample obj;
obj.value = 10;
cout << obj.*ptr;
Output
10Explanation:
The pointer does not store a memory address directly—it stores member location information relative to an object.
When Is Pointer-to-Member Useful?
- When member access must be decided at runtime
- In generic programming
- In plugin-based architectures
Using Special C Operators
c
#include
// Function to demonstrate the comma operator
void demoCommaOperator() {
int a, b;
b = (a = 5, a + 10);
printf("Value of b using comma operator: %d
", b);
}
// Demonstrating the pointer-to-member operator (only relevant in C++)
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
void demoPointerToMember() {
struct Point p = {10, 20};
struct Point* ptr = &p;
printf("Point x: %d, Point y: %d
", ptr->x, ptr->y);
}
int main() {
demoCommaOperator();
demoPointerToMember();
return 0;
}
Explanation of the Code
This code displays two interesting operators in C. Let’s break it down:
- The `demoCommaOperator` function showcases the comma operator. Here, `a` is first assigned with `5` and then immediately used to compute `a + 10`. The result, `15`, is assigned to `b`. The comma operator evaluates each expression in sequence, returning the last expression’s result. This is handy for executing multiple operations within a single statement.
- Next, the `demoPointerToMember` function explores the pointer-to-member operator. While specific to C++, it demonstrates how to access `struct` members via pointers. A `Point` structure is defined with `x` and `y`. A `Point` instance `p` is created and a pointer `ptr` is set to `p`. The `->` operator bypasses the need for dereferencing with `*`, making it convenient for accessing members like `x` and `y` directly from a pointer to a `struct`.
Output
Value of b using comma operator: 15
Point x: 10, Point y: 20Pros & Cons of Special Operators in C
| Operator | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Comma Operator | Compact code, useful in loops | Reduces readability |
| Pointer-to-Member | Flexible object access | Complex syntax |
| Traditional Access | Easy to read | Less dynamic |
Real-Life Applications of Special Operators in C
/.,mnv
- Efficient Data Collection in Embedded Systems – Apple’s HomeKit:
When efficiently managing sensor data, embedded systems use the comma operator to sequentially evaluate expressions in a single line. This becomes quite handy. Apple’s HomeKit uses this to streamline data processes from smart devices.
Output: The result shows updated temperature readings while also chaining operations, which is 30.int fetchData() {
int temperatureSensor = 25, humiditySensor = 60;
return (temperatureSensor += 5, humiditySensor += 10), temperatureSensor;
} - Efficient Execution in Game Development – EA Sports:
Pointer-to-member operators are used to optimise accessing game object properties. EA Sports often applies this in their high-intensity games to improve performance by reducing processing time.
class Player {
public:
int score;
};
int main() {
Player Ronaldo;
Ronaldo.score = 92;
int Player::*scorePtr = &Player::score;
Ronaldo.*scorePtr = 95;
return Ronaldo.score;
}
Output: By directly altering the player score using a pointer-to-member, developers achieve the new score of 95 efficiently.
(-
- Data Updates in Finance Systems – PayPal’s Transaction Analysis:
Finance systems benefit from the comma operator when updating large transactions lists smoothly. PayPal incorporates this for real-time transaction processing.
Output: Transactions are marked complete with resulting states being updated quickly and accurately.int updateTransactionState() {
int transactionCompleted = 0, transactionPending = 1;
return (transactionCompleted = 1, transactionPending = 0);
}
Special Operators in C Questions
- What is the comma operator in C, and how does it work in loop constructs? The comma operator in C allows multiple expressions to be evaluated in a single statement. The value of the last expression is returned. It’s particularly useful in scenarios like loop constructs where you might want to increment two variables concurrently. For example:
for (int i = 0, j = 10; i < j; i++, j--) {
printf("i: %d, j: %d
", i, j);
}
In this snippet, both `i` and `j` are incremented and decremented, respectively, in every loop iteration. - How does the pointer-to-member operator work in structures? The pointer-to-member operator (`->`) is used to access members of a structure or union through a pointer. If you have a structure `Student` with a member `name`, you can access it using a pointer like so:
struct Student *sPtr;
sPtr->name; // Equivalent to (*sPtr).name;
This is handy when working with dynamic structures in C. - Can the comma operator affect the control flow in switch statements? Yes, though it’s unconventional. By using the comma operator, you can execute multiple expressions and influence the flow of logic within a case. However, because it’s rarely used this way, it’s generally more appropriate to stick to traditional statements within switch cases for clarity.
- Is there a performance impact when using the comma operator in expressions? The performance impact of using the comma operator is generally negligible since each expression is still evaluated as it would be in individual statements. However, from a readability perspective, packing too many expressions might lead to less maintainable code.
Our AI-powered c’ online compiler is revolutionising the coding experience! Instantly write, run, and test your code with the help of AI, providing real-time feedback and improvements. Elevate your coding journey by harnessing the power of AI to enhance efficiency and understanding in a user-friendly environment.
Conclusion
Completing ‘Special Operators in C’ empowers you to write cleaner, more efficient code, boosting your problem-solving skills. You’ll gain confidence in tackling advanced coding challenges. Dive deeper into the programming world; explore languages like Java, Python, C++, and more at Newtum for continuous learning and growth.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.


