To multiply two numbers in Python, simply use the * operator. For example: result = 5 * 3 will yield 15.
Understanding basic arithmetic operations like multiplication is crucial for Python beginners. It’s foundational for more complex programming tasks, from data analysis to game development.
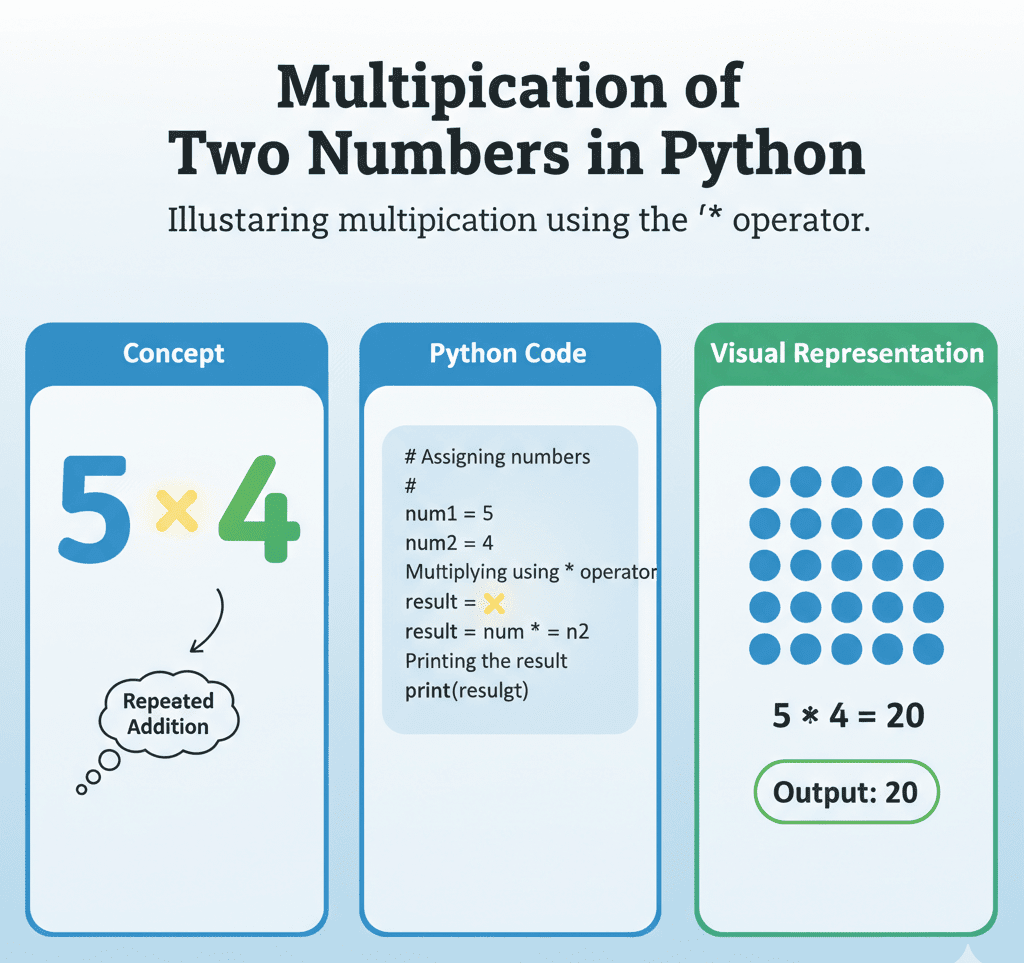
Quick Summary of Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python
- Operator Used:
* - Data Types Supported: Integers, Floats
- Common Use Cases: Calculations, Algorithms, Data Processing
What is the Multiplication Operator in Python?
Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python: Basic Syntax
Python uses the * operator to multiply numbers. It’s simple and works with both integers and floats.
Example:
result = 4 * 2 print(result) # Output: 8
Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python -Handling Different Data Types
Python allows multiplication of integers, floating-point numbers, and even combinations of both.
Example:
result = 4.5 * 2 print(result) # Output: 9.0
Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python User Input Multiplication
You can take input from users and multiply numbers after converting them to numeric types.
Example:
num1 = float(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = float(input("Enter second number: "))
print(f"Product: {num1 * num2}")
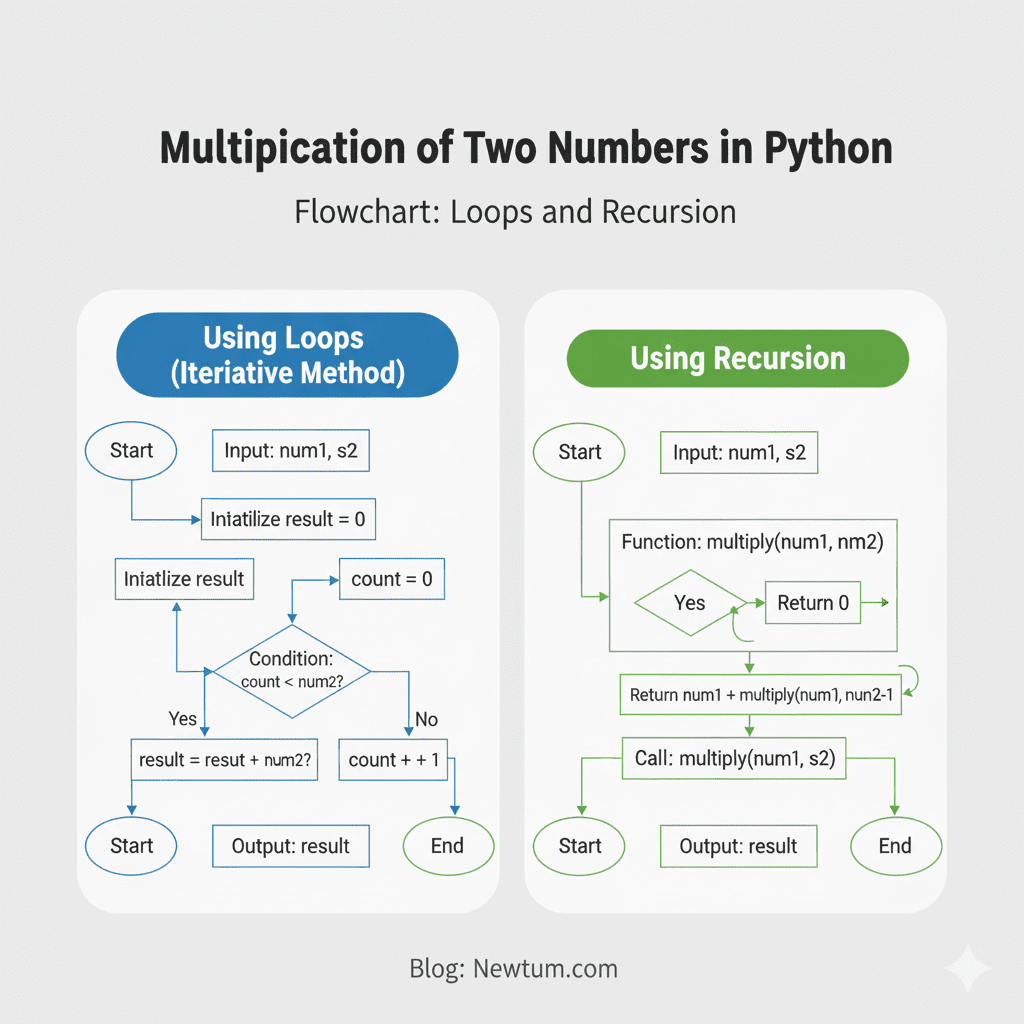
Alternative Methods for Multiplication
Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python Using Loops (Repeated Addition)
Multiplication can be implemented by adding a number repeatedly, which helps beginners understand the logic behind multiplication.
Example:
def multiply(num1, num2):
result = 0
for _ in range(int(num2)):
result += num1
return result
print(multiply(4, 3)) # Output: 12
Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python Using Recursion
Recursion can also perform multiplication by breaking the problem into smaller additions.
Example:
def multiply(num1, num2):
if num2 == 0:
return 0
return num1 + multiply(num1, num2 - 1)
print(multiply(4, 3)) # Output: 12
Our AI-powered python online compiler offers a seamless coding experience. Instantly write, run, and test code with AI assistance. It empowers users to code more efficiently by providing immediate feedback and suggestions, making it ideal for both beginners and experienced programmers looking to optimise their coding workflow.
Practical Example of Using Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python
Python multiplication is widely used in real-world applications across various industries. Here are some examples:
1. Amazon – E-commerce Sales Calculations
Amazon uses Python scripts to calculate total sales, inventory, and discounts. Multiplication helps compute the total price for multiple items.
Example:
quantity = 120
price_per_item = 15.5
total_price = quantity * price_per_item
print(f"Total Price: {total_price}")
Output:
Total Price: 1860.0Usage: This allows Amazon to quickly compute order totals, manage stock, and generate invoices efficiently.
2. Netflix – Data Analytics for Recommendations
Netflix uses Python for data analytics and personalized recommendations. Multiplication is used to scale viewing metrics, calculate weighted scores, or predict ratings.
Example:
rating_score = 4.5
weight_factor = 3
weighted_score = rating_score * weight_factor
print(f"Weighted Score: {weighted_score}")
Output:
Weighted Score: 13.5Usage: Helps Netflix prioritize content and improve recommendation accuracy for users.
3. Financial Companies – Interest and Profit Calculations
Banks and fintech companies like PayPal or Square use multiplication for interest calculation, loan processing, or investment growth.
Example:
principal = 1000
rate = 0.05
time = 3
interest = principal * rate * time
print(f"Interest: {interest}")
Output:
Interest: 150.0Usage: Automates financial calculations, saving time and reducing errors.
This section highlights practical applications of multiplication of two numbers in Python in industry scenarios, showing readers its real-world relevance.
Pros & Cons of multiplication of two numbers in Python
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
* Operator | Simple, efficient | Limited to numeric types |
| Loop Method | Demonstrates logic clearly | Less efficient for large numbers |
| Recursion | Elegant solution | Risk of stack overflow |
FAQ of Multiplication of Two Numbers in Python
Q1: Can I multiply more than two numbers at once in Python?
A: Yes! You can multiply multiple numbers using the * operator in a single expression or by using the math.prod() function for lists.
Example:
import math numbers = [2, 3, 4] result = math.prod(numbers) print(result) # Output: 24
Q2: What happens if I multiply a string by a number in Python?
A: Multiplying a string by an integer repeats the string.
Example:
text = "Hi! " print(text * 3) # Output: Hi! Hi! Hi!
Q3: How do I multiply user input without converting to float first?
A: Python input is always a string. To multiply numbers correctly, convert input to int or float. Without conversion, multiplication will throw an error.
Example:
num1 = int(input("Enter first number: "))
num2 = int(input("Enter second number: "))
print(num1 * num2)
Q4: Can I multiply negative numbers in Python?
A: Yes, Python handles negative numbers naturally. Multiplying a negative by a positive gives a negative result; multiplying two negatives gives a positive result.
Example:
print(-5 * 3) # Output: -15 print(-5 * -3) # Output: 15
Q5: How do I multiply numbers in a list without a loop?
A: Use Python’s math.prod() function to multiply all elements of a list efficiently without a loop.
Example:
import math numbers = [2, 5, 3] result = math.prod(numbers) print(result) # Output: 30
Engagement & Conversion Layer
Python’s multiplication operator is simple yet powerful, forming the foundation for countless real-world applications. Mastering it opens doors to coding confidence and problem-solving skills. Explore more Python tutorials, tips, and projects by visiting Newtum to continue your programming journey.
For More Python Programming Exercises and Solutions check out our Python Exercises and Solutions



