Assignment operators in C are used to assign values to variables efficiently. They combine arithmetic or bitwise operations with assignment, simplifying code and reducing repetition.
Whether you’re writing your first “Hello World” program or building complex algorithms, assignment operators are everywhere in C. They make code cleaner, faster, and easier to read — a must-know concept for every C programmer. Understanding them helps you write smarter, more optimized programs.
Key Takeaways of Assignment Operators in C
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| = | Simple Assignment | x = 10 | x becomes 10 |
| += | Add and Assign | x += 5 | x = x + 5 |
| -= | Subtract and Assign | x -= 3 | x = x – 3 |
| *= | Multiply and Assign | x *= 2 | x = x * 2 |
| /= | Divide and Assign | x /= 4 | x = x / 4 |
| %= | Modulus and Assign | x %= 3 | x = x % 3 |
What Are Assignment Operators in C?
Assignment operators in C are symbols used to assign the value of an expression to a variable.
They help simplify code by combining operations like addition or multiplication with assignment — reducing redundancy and improving performance.
For example, instead of writing:
x = x + 10;
You can write:
x += 10;
Both statements achieve the same result, but the second one is shorter and easier to read.
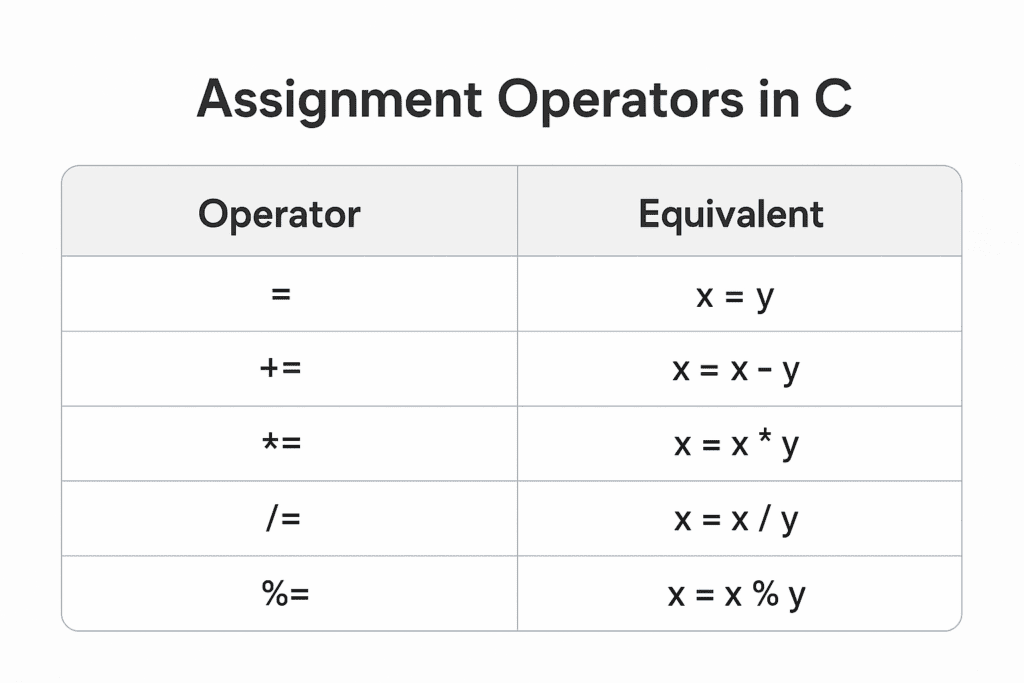
Types of Assignment Operators in C
C provides several types of assignment operators to make coding more efficient.
| Operator | Description | Example | Equivalent Expression |
|---|---|---|---|
= | Assigns right-hand value to left-hand variable | x = 10; | x = 10 |
+= | Adds and assigns value | x += 5; | x = x + 5 |
-= | Subtracts and assigns value | x -= 3; | x = x – 3 |
*= | Multiplies and assigns value | x *= 2; | x = x * 2 |
/= | Divides and assigns value | x /= 4; | x = x / 4 |
%= | Finds remainder and assigns value | x %= 3; | x = x % 3 |
These operators are also known as compound assignment operators because they combine an arithmetic or bitwise operation with assignment.
How Do Compound Assignment Operators Work?
Compound assignment operators perform two operations in one step —
1️⃣ They first execute the arithmetic or bitwise operation.
2️⃣ Then, they store the result back into the same variable.
For instance, the operator x += y means:
x = x + y;
So, it adds the value of y to x and updates x with the new result.
Using compound operators can make your code shorter and often more efficient, especially in loops or mathematical computations.
Example Program
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x = 10;
x += 5; // Same as x = x + 5
printf("After += operator: %d\n", x);
x -= 2; // Same as x = x - 2
printf("After -= operator: %d\n", x);
x *= 3; // Same as x = x * 3
printf("After *= operator: %d\n", x);
x /= 4; // Same as x = x / 4
printf("After /= operator: %d\n", x);
x %= 3; // Same as x = x % 3
printf("After %%= operator: %d\n", x);
return 0;
}
Output:
After += operator: 15
After -= operator: 13
After *= operator: 39
After /= operator: 9
After %= operator: 0This example shows how each assignment operator updates the variable value step-by-step.
Pros & Cons of Assignment Operators in C
| Operator Type | Advantage | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
Simple Assignment (=) | Easy to use | Repetitive for math ops |
Compound Assignment (+=, etc.) | Shorter, faster | Less readable for beginners |
Practical Uses of Assignment Operators in C
- Google’s Search Algorithm Optimisation
In enhancing their search algorithm, Google uses assignment operators to update iterative variables, counters, and flags. This process is crucial in weighing search results for relevance. Consider a simple example within their codebase where an assignment operation updates a relevance score.
The output leads to tailored search results that better match user queries.int relevanceScore = 0;
relevanceScore += 10;
// Assigns a new relevance score based on certain criteria. - Facebook’s Post Engagement Tracking
Facebook uses assignment operators to track and display post interactions, such as likes and comments, in real-time. By incrementing counters efficiently, they provide users with immediate updates on post interactions.
This output helps ensure users see real-time engagement numbers.int likes = 100;
likes += 5;
// Updates the count when new likes are received. - Amazon’s Inventory Management System
To manage inventory dynamically, Amazon leverages assignment operators. This helps in adjusting stock levels as orders are placed and deliveries are received.
The output guarantees stock levels are up-to-date across their massive logistics chain.int stock = 150;
stock -= 10;
// Deducts from current stock when an item is sold.
Assignment Operators in C: FAQ
Understanding assignment operators in C can sometimes be a real head-scratcher, especially if you’re just starting out or even if you’re diving deeper into the world of C programming. Here are a handful of less commonly addressed questions that often pop up on Google, Reddit, and Quora. These tackle some of the finer points of using assignment operators effectively.
- What’s the difference between ‘=’ and ‘==’ in C?
The ‘=’ operator is for assigning values. It sets the variable on its left side to the value on its right side. For example,a = 5;assigns 5 toa. On the other hand, ‘==’ is a comparison operator used to check if two values are equal. You’d use it like this:if(a == 5) { ... }
There’s no assignment happening here, just a question being asked. - Can assignment operators be overloaded in C?
No, C doesn’t support operator overloading. This means you can’t redefine how assignment operators work. If you need custom behaviour, you might need to structure your code differently. - How do assignment operators behave with different data types?
In C, when using assignment operators, they perform implicit type conversion or casting if the data types differ on either side. For example,int a; float b = 2.5; a = b;would convertbto an integer before assignment. - What happens if I use assignment in a conditional statement?
Using an assignment operator in a conditional, likeif(a = 1)
, assigns 1 toaand then evaluates the value. This often leads to unexpected logic errors if you’re actually trying to compare equality. - Are compound assignment operators more efficient in C?
Yes! Compound operators like+=are typically more efficient because they combine assignment and operation into a single statement. This can lead to faster execution, especially in loops. - What is the purpose of the comma operator in assignments?
The comma operator lets you perform multiple operations in a single statement. But in an assignment, only the last expression is assigned. For instance,a = (1, 2, 3);assigns 3 toaafter evaluating all other values. - How do different compilers handle compound assignment operators?
Most compilers handle compound assignment operators in a standard way, as defined by the C language. However, some may optimally convert them based on architecture or target performance enhancements. - Can assignment operators lead to undefined behaviour in C?
Yes, using assignment operators without considering precedence and side-effects can result in undefined behaviour. For instance, expressions likei = i++should be avoided as their behaviour can be unpredictable.
These are, of course, just a few of the fascinating corners where the assignment operators get intriguing!
Our AI-powered c online compiler lets users instantly write, run, and test code seamlessly. Experience unparalleled efficiency and smooth learning without the hassle of setup. Accessible and intuitive, it’s perfect for anyone looking to dive into coding with real-time AI assistance. Give it a try today!
Conclusion
Assignment Operators in C empower programmers to handle data efficiently, enhancing coding skills and boosting confidence. Mastering these operators is a rewarding step that demystifies programming logic. Dive into coding and explore more languages like Java and Python on Newtum for endless learning possibilities.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.