To delete a file in Python, you can use os.remove() or Path.unlink() from the pathlib module. These methods permanently remove a file from your system, so it’s important to check whether the file exists before deleting it to avoid errors.
Deleting files programmatically is a common requirement in modern applications—from log cleanup scripts and data pipelines to backend services and DevOps automation.
As Python continues to dominate scripting, AI, and cloud workflows, knowing how to safely delete files prevents crashes, data loss, and production issues. This guide walks you through modern, safe, and beginner-friendly ways to delete files in Python.
Key Takeaways of Delete a File in Python
Quick Summary:
os.remove()→ Traditional, widely used file deletionos.unlink()→ Same asos.remove()pathlib.Path.unlink()→ Modern, readable, Pythonic- Always check file existence before deleting
- Handle exceptions to avoid runtime crashes
✅ Best practice: Use pathlib for new Python projects.
What does “delete a file in Python” mean?
Deleting a file in Python means permanently removing a file from the operating system’s file system using Python’s built-in libraries. Once a file is deleted, it cannot be recovered unless you have a backup or version control in place.
This operation is commonly used in:
- Automation scripts
- Log and cache cleanup
- Data processing pipelines
- Backend and DevOps workflows
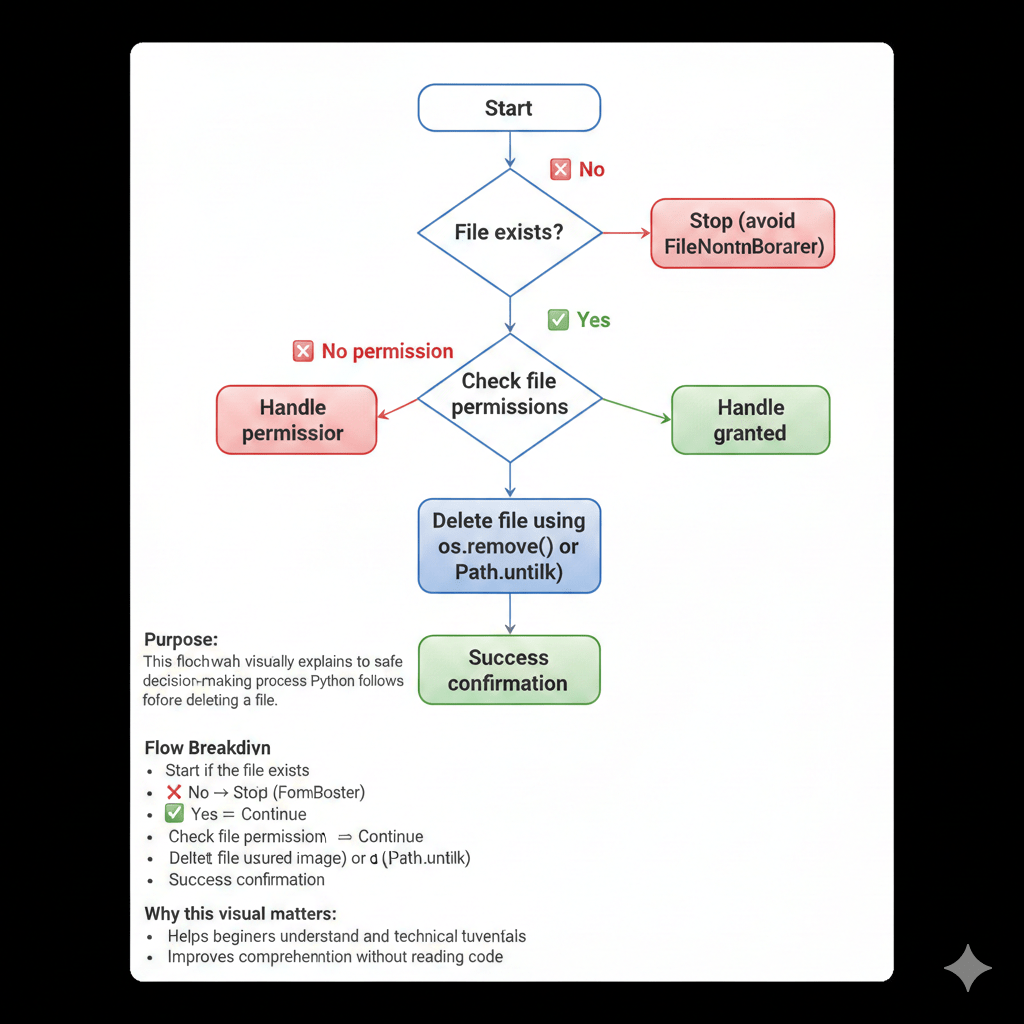
How do you delete a file in Python using os.remove()?
The os module provides low-level file and directory operations that work across different operating systems.
Example: Delete a file using os.remove()
import os
os.remove("example.txt")
This command immediately deletes the file named example.txt from the current directory.
📌 Important:
If the file does not exist, Python raises a FileNotFoundError. If you don’t have permission, a PermissionError will occur.
How to delete a file in Python using pathlib?
The pathlib module provides a modern, object-oriented, and more readable way to work with files and paths in Python.
Example: Delete a file using pathlib
from pathlib import Path
file_path = Path("example.txt")
file_path.unlink()
Why use pathlib?
✔ Recommended for Python 3.6+
✔ Cleaner and more readable syntax
✔ Easier path handling across operating systems
For new Python projects, pathlib is considered a best practice.
How do you check if a file exists before deleting it?
To avoid runtime errors, always verify that a file exists before attempting to delete it.
Example: Safe file deletion in Python
from pathlib import Path
file_path = Path("example.txt")
if file_path.exists():
file_path.unlink()
This approach prevents:
FileNotFoundError- Script crashes
- Unexpected production failures
It is especially important in automation and scheduled jobs.
What errors occur when deleting files in Python?
When deleting files in Python, you may encounter the following common errors:
- FileNotFoundError → The file does not exist
- PermissionError → Insufficient rights to delete the file
- IsADirectoryError → Attempting to delete a folder instead of a file
Handling these exceptions properly improves script reliability and makes your application safer for real-world use.
Python File Deletion Code
python
import os
file_path = "sample.txt"
try:
os.remove(file_path)
print("File deleted successfully.")
except FileNotFoundError:
print("The file was not found.")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
Explanation of the Code
This code is a basic Python script for removing files from a directory. Here’s a breakdown of each part:
- The script starts by using the `os` module, which contains functions to interact with the operating system. Importing this module enables us to perform file operations.
- We specify the `file_path` variable, setting it to the file name “sample.txt”. This is the file we’ll attempt to delete.
- A `try` block then attempts to remove the file using `os.remove(file_path)`. If successful, it prints “File deleted successfully.”
- If the file isn’t found, a `FileNotFoundError` is raised. The code catches this error and informs the user with a friendly message: “The file was not found.”
- For any other unexpected exceptions, it catches them with a generic `Exception` and prints a tailored error message for further investigation.
Output
The file was not found.Delete a File in Python: Comparison of os.remove () and pathlib. unlink()
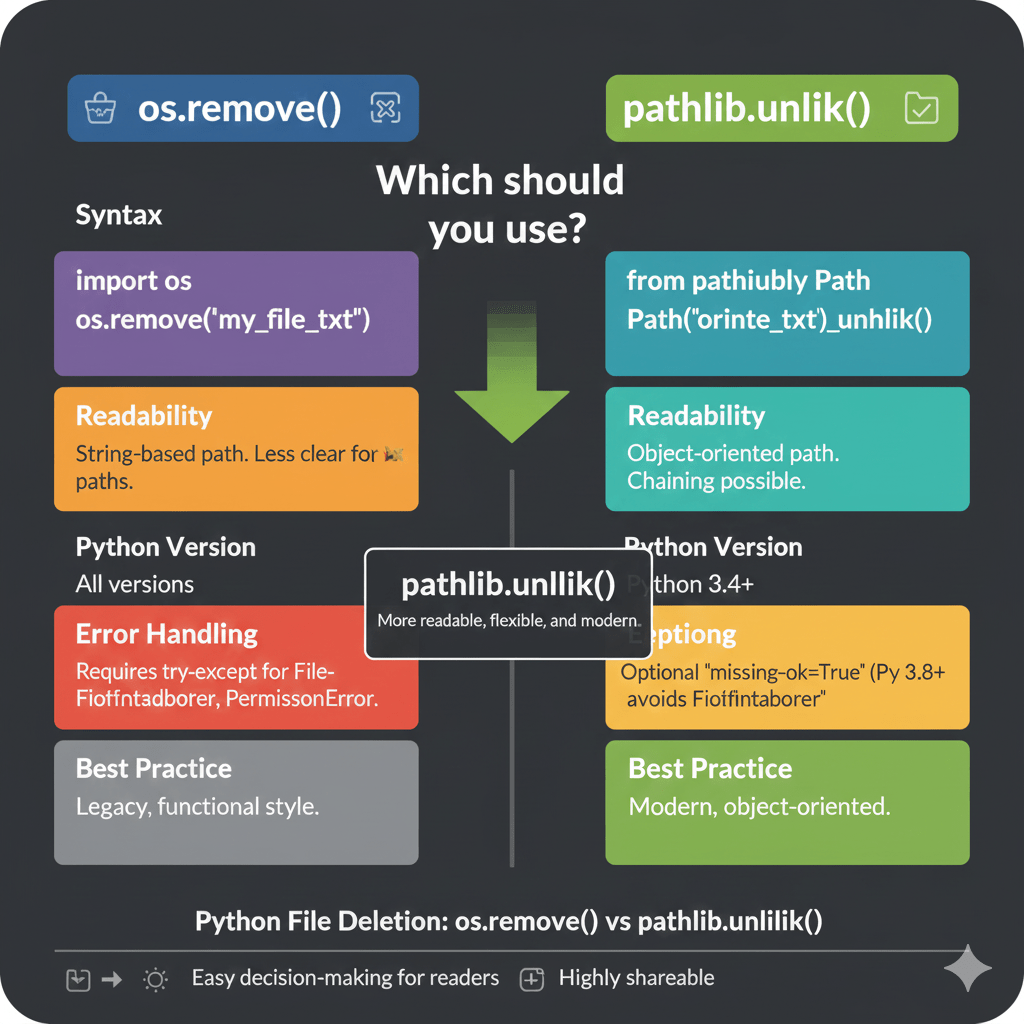
🆚 os.remove() vs pathlib.unlink()
| Feature | os.remove() | pathlib.unlink() |
|---|---|---|
| Readability | Moderate | High |
| Python Version | All | Python 3.4+ |
| Error Handling | Manual | Cleaner |
| Modern Style | ❌ | ✅ |
| Recommended | ⚠️ | ✅ |
📌 Winner: pathlib.unlink() for modern Python projects
Real-Life Uses for Deleting Files with Python
🏢 Companies & Real-World Use Cases
Python file deletion is widely used by large tech companies to automate storage management and improve system performance.
- Netflix → Deletes temporary data files after ETL jobs to prevent unnecessary storage consumption in data pipelines.
- Google → Uses Python scripts to clean and rotate massive log files generated by backend services.
- Dropbox → Automates file lifecycle management, removing outdated or synced files efficiently.
These companies rely on Python’s file deletion capabilities to maintain scalable, cost-efficient infrastructure.
🔧 Example: Log Cleanup Script in Python
A common real-world scenario is automatically deleting old log files to free up disk space.
Python Code Example
from pathlib import Path
log_file = Path("old_log.log")
if log_file.exists():
log_file.unlink()
print("Log file deleted successfully")
Output
Log file deleted successfully
✅ Why This Matters in Production
✔ Reduces unnecessary storage usage
✔ Prevents performance issues caused by oversized logs
✔ Commonly used in DevOps, cloud automation, and backend maintenance
✔ Improves reliability of long-running applications
This simple pattern is often embedded in cron jobs, CI/CD pipelines, and monitoring systems, making it a practical and essential Python skill.
Real DevOps Example: Automating File Deletion with a Cron Job
In DevOps and cloud environments, Python file deletion scripts are commonly executed using cron jobs to automate routine cleanup tasks such as removing old logs or temporary files.
📌 Scenario
A server generates log files daily. To prevent disk space issues, logs older than a specific period must be deleted automatically.
🔧 Step 1: Python Log Cleanup Script
from pathlib import Path
import time
LOG_DIR = Path("/var/log/myapp")
DAYS_OLD = 7
current_time = time.time()
for log_file in LOG_DIR.glob("*.log"):
if log_file.is_file():
file_age = current_time - log_file.stat().st_mtime
if file_age > DAYS_OLD * 86400:
log_file.unlink()
print(f"Deleted: {log_file.name}")
What this script does:
- Scans a log directory
- Identifies
.logfiles - Deletes files older than 7 days
- Prints the deleted file names
🗓️ Step 2: Schedule the Script Using Cron
Edit the crontab:
crontab -e
Add the cron job:
0 2 * * * /usr/bin/python3 /home/user/cleanup_logs.py >> /home/user/cleanup.log 2>&1
Cron breakdown:
0 2 * * *→ Runs daily at 2:00 AM/usr/bin/python3→ Python interpreter pathcleanup_logs.py→ Cleanup script- Output logged for monitoring
🚀 Output (Example)
Deleted: app_2024_12_01.log Deleted: app_2024_12_02.log
✅ Why DevOps Teams Use This Approach
✔ Fully automated file cleanup
✔ Prevents disk exhaustion outages
✔ Zero manual intervention
✔ Works on Linux servers, VMs, and cloud instances
✔ Standard practice in AWS, GCP, Azure, and on-prem servers
Delete a File in Python Questions
- What is the simplest way to delete a file in Python?
The simplest way to delete a file in Python is by using theos.remove()method from the os module. Here’s a quick example:import os
file_path = 'path/to/your/file.txt'
os.remove(file_path) - Can you delete a file in Python without importing libraries?
No, to delete a file in Python, you need to use built-in libraries like os or pathlib. - What happens if I try to delete a file that doesn’t exist?
Attempting to delete a non-existent file withos.remove()will raise aFileNotFoundErrorexception. Handling exceptions can prevent your program from crashing:try:
os.remove(file_path)
except FileNotFoundError:
print("File does not exist.") - Is it possible to permanently delete a file with Python?
Yes, when you useos.remove(), the file is permanently deleted from the file system unless it’s recoverable through external recovery tools. - Can I delete a file in Python if it is being used by another process?
Deleting a file that is open in another process may cause an error, especially on Windows systems. It’s generally not recommended and can lead to data loss. - How do I check if a file exists before deleting it?
You can useos.path.exists()to check for a file’s existence:if os.path.exists(file_path):
os.remove(file_path)
else:
print("The file does not exist.") - Can you use a wildcard to delete multiple files in Python?
Using the glob module allows for wildcard usage. Here’s a quick example:import glob
for file in glob.glob("*.txt"):
os.remove(file) - What module provides an object-oriented method to delete a file?
Thepathlibmodule in Python provides an object-oriented method for file manipulation, including deletion:from pathlib import Path
file = Path('path/to/your/file.txt')
file.unlink()
Discover the power of our AI-enhanced python online compiler. Instantly write, run, and test your code with built-in artificial intelligence features. No need for multiple tools, everything you need is right at your fingertips, making the coding process more efficient and intuitive than ever before.
Conclusion
“Delete a File in Python” is a simple yet empowering task that builds essential coding skills. Give it a go and relish the satisfaction of mastering a core function. For a deeper dive into programming languages like Java, Python, C, C++, and more, explore Newtum.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.



