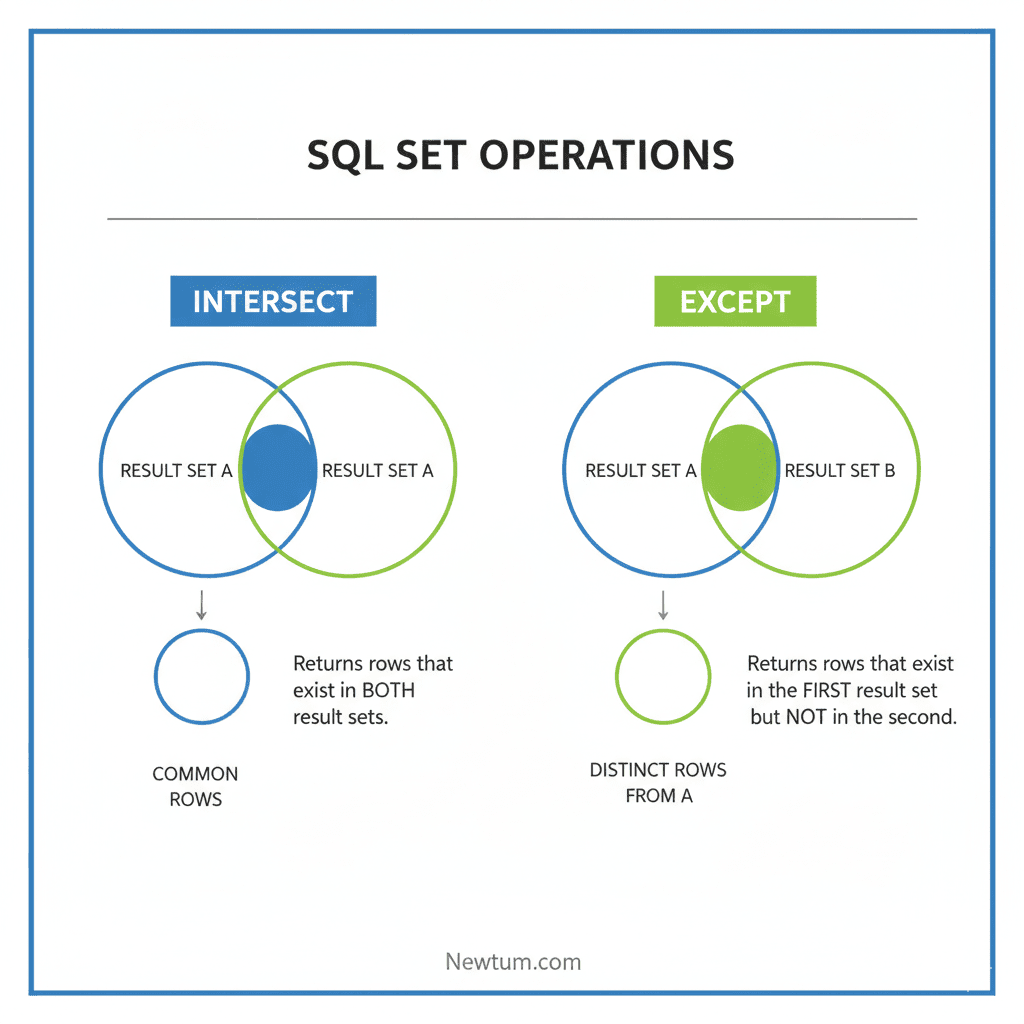
INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL are set operators used to combine query results. INTERSECT returns common rows between queries, while EXCEPT returns rows from the first query that don’t exist in the second.
Understanding INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL is crucial for database analysts and developers who need precise control over query results. These operators simplify comparing datasets, detecting duplicates, and filtering unique records efficiently, making reporting and data analysis faster and more accurate.
Key Takeaways of Intersect and Except in SQL
| Operator | Functionality | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| INTERSECT | Returns rows common to both queries | Find employees in both Sales & HR |
| EXCEPT | Returns rows in first query not in second | List customers who didn’t order yet |
What is INTERSECT in SQL?
INTERSECT is a SQL set operator that returns all rows common between two SELECT statements. Duplicate rows are automatically removed, making it perfect for identifying overlaps between datasets.
Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table1 INTERSECT SELECT column_name FROM table2;
Example
SELECT EmployeeID FROM Sales INTERSECT SELECT EmployeeID FROM HR;
Output: Returns a list of employees working in both Sales and HR.
What is EXCEPT in SQL?
EXCEPT is a SQL set operator that returns rows from the first SELECT query that do not appear in the second. It is commonly used to find unique or missing records between datasets.
Syntax
SELECT column_name FROM table1 EXCEPT SELECT column_name FROM table2;
Example
SELECT CustomerID FROM Orders2025 EXCEPT SELECT CustomerID FROM Orders2024;
Output: Returns customers who placed orders in 2025 but not in 2024.
Differences Between INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL
| Feature | INTERSECT | EXCEPT |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Returns common rows | Returns unique rows from first query |
| Output | Only shared records | Records not in the second set |
| Use Case | Identifying overlaps | Detecting missing or new data |
Working with INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL
sql
-- Create table employees
CREATE TABLE employees (
employee_id INT,
first_name VARCHAR(50),
last_name VARCHAR(50),
department VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Create table employees_project
CREATE TABLE employees_project (
employee_id INT,
project_id INT,
project_name VARCHAR(50)
);
-- Insert sample data into employees
INSERT INTO employees (employee_id, first_name, last_name, department) VALUES
(1, 'John', 'Doe', 'Engineering'),
(2, 'Jane', 'Smith', 'HR'),
(3, 'James', 'Brown', 'Engineering'),
(4, 'Emily', 'Davis', 'Finance');
-- Insert sample data into employees_project
INSERT INTO employees_project (employee_id, project_id, project_name) VALUES
(1, 101, 'Project A'),
(2, 102, 'Project B'),
(3, 101, 'Project A'),
(5, 103, 'Project C');
-- Use INTERSECT to get employees who are both in Engineering department and involved in Project A
SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE department = 'Engineering'
INTERSECT
SELECT employee_id FROM employees_project WHERE project_name = 'Project A';
-- Use EXCEPT to get employees in Engineering department but not involved in any projects
SELECT employee_id FROM employees WHERE department = 'Engineering'
EXCEPT
SELECT employee_id FROM employees_project;
Explanation of the Code
Here’s a breakdown of the provided SQL code using an ordered list for clarity:
- Create two tables:
- `employees` includes ID, first name, last name, and department.`employees_project` contains employee IDs, project IDs, and project names.
- Insert sample data into each table.
- The `employees` table includes individuals from various departments.The `employees_project` table logs project involvement.
- Use the `INTERSECT` statement to find and return employees in the “Engineering” department also working on “Project A”.
- Implement the `EXCEPT` statement to identify “Engineering” employees not participating in any projects. This demonstrates how `INTERSECT` and `EXCEPT` help filter specific subsets of data for targeted analysis.
Output
employee_id
1
3
employee_id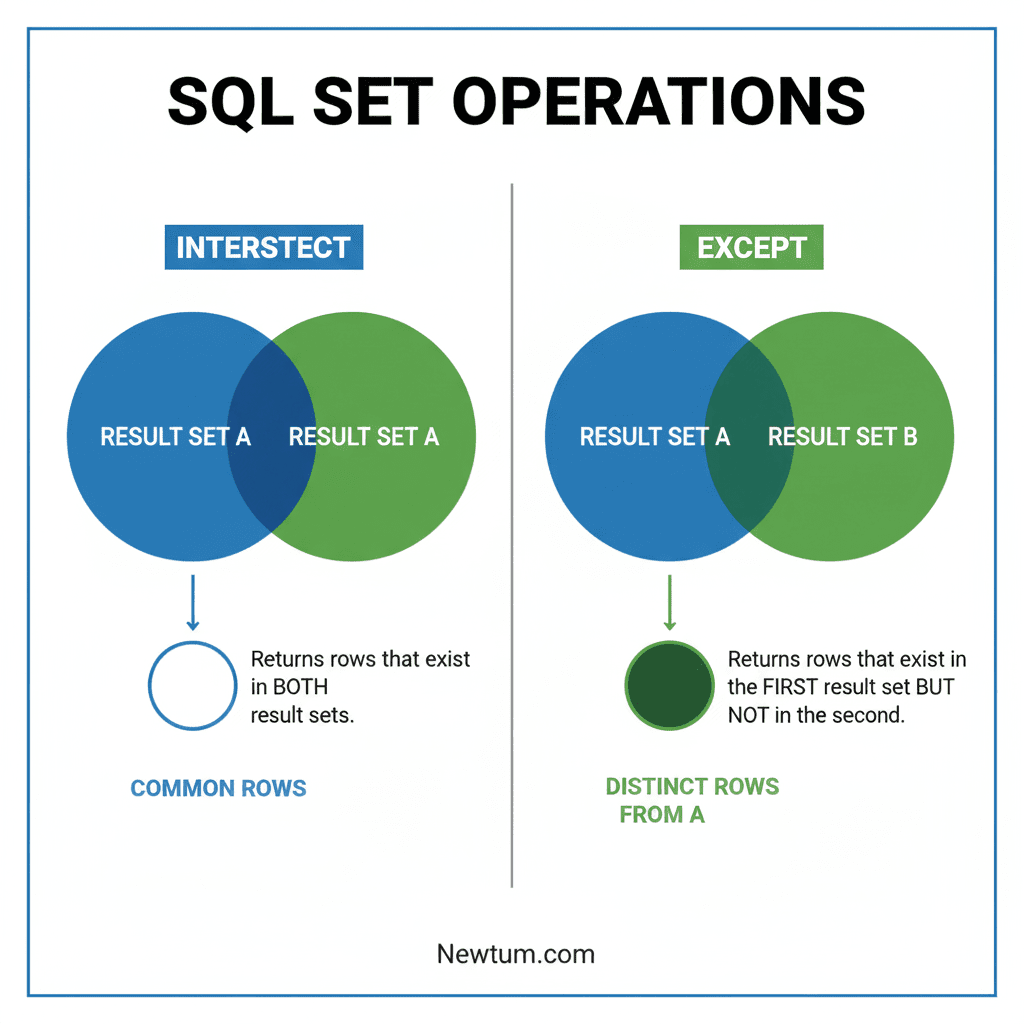
Practical Applications of INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL
Understanding how INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL work isn’t just academic — these operators are widely used by top organizations to manage data, detect discrepancies, and ensure data integrity across systems.
Example 1: Microsoft (Data Comparison Across Departments)
Use Case: Microsoft’s internal HR and Sales departments often need to identify employees involved in both sales operations and internal training programs.
Code Example:
SELECT EmployeeID FROM SalesTeam INTERSECT SELECT EmployeeID FROM TrainingProgram;
Output: List of employees participating in both teams — helping Microsoft streamline recognition programs and internal audits.
Example 2: Amazon (Customer Segmentation for Marketing)
Use Case: Amazon analysts compare order data between two years to identify new customers.
Code Example:
SELECT CustomerID FROM Orders2025 EXCEPT SELECT CustomerID FROM Orders2024;
Output: A dataset of customers who ordered only in 2025.
Benefit: Helps Amazon’s marketing team target first-time buyers with loyalty campaigns.
Example 3: Netflix (Subscription Insights)
Use Case: Netflix uses INTERSECT to find users subscribed to multiple premium plans or testing overlapping features.
Code Example:
SELECT UserID FROM PremiumPlan INTERSECT SELECT UserID FROM FamilyPlan;
Output: Identifies overlapping users to prevent billing duplication and optimize plan management.
Example 4: Banking Sector (Fraud Detection)
Use Case: Banks use EXCEPT to find mismatches between customer transactions and account activity logs.
Code Example:
SELECT AccountID FROM Transactions EXCEPT SELECT AccountID FROM VerifiedLogs;
Output: Returns accounts with unverified transactions — crucial for fraud analysis and compliance.
These practical scenarios show how INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL simplify complex data analysis, improve decision-making, and maintain operational efficiency across industries like e-commerce, finance, and entertainment.
INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL Interview Focus
When diving into SQL, particularly when dealing with operations like INTERSECT and EXCEPT, there’s always something new to learn. If you’ve been trawling through forums like Reddit or Q&A sites such as Quora, you might’ve come across some intriguing but less explored questions about these two SQL keywords. Let’s tackle these head-on with some fresh perspectives and examples.
- What’s the difference between INTERSECT and a simple JOIN in SQL? The INTERSECT operation retrieves only the rows that are common to both SQL queries, whereas a JOIN can return rows that combine columns from different tables based on a related column. Here’s an INTERSECT example:
- Can INTERSECT or EXCEPT handle NULL values? Yes, both INTERSECT and EXCEPT consider NULL values during their operations. In INTERSECT, a NULL must appear in the same columns across both queries to be included. In EXCEPT, NULL values present in the first query but not the second will be returned.
- How can I use INTERSECT to find duplicate rows in two tables? Use INTERSECT when you want to retrieve exact matches of rows present in two different tables:
- What’s a real-world use case for EXCEPT in SQL? An example would be identifying users in one database table who haven’t performed a particular action tracked in another table:
- Can you chain INTERSECT and EXCEPT together in one query? Yes, but it requires careful query structuring. Each operation needs to be part of its own SELECT statement, like this:
- How do performance considerations compare between INTERSECT, EXCEPT, and JOINs? Unlike JOINs, INTERSECT and EXCEPT typically work with datasets where you need exact row matches across queries. They may perform differently based on databases’ internal optimizations and indices, so testing execution plans is wise for efficiency.
- Are there any database systems that do not support INTERSECT or EXCEPT? Most relational databases such as PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and Oracle support INTERSECT and EXCEPT. However, some databases like MySQL do not support these operations directly, so you’d need to find alternative ways like using JOINs.
- How can I simulate INTERSECT in databases that don’t support it? Use a JOIN with GROUP BY to mimic INTERSECT. This example simulates INTERSECT using MySQL via INNER JOIN:
SELECT column1 FROM table1
INTERSECT
SELECT column1 FROM table2;A JOIN might look like this:
SELECT table1.column1, table2.column2
FROM table1
JOIN table2
ON table1.id = table2.id;SELECT * FROM table1
INTERSECT
SELECT * FROM table2;
SELECT user_id FROM all_users
EXCEPT
SELECT user_id FROM action_tracked_users;
(SELECT column1 FROM table1
INTERSECT
SELECT column1 FROM table2)
EXCEPT
(SELECT column1 FROM table3); SELECT a.column1
FROM table1 a
INNER JOIN table2 b
ON a.column1 = b.column1;Our AI-powered sql online compiler allows users to effortlessly write, run, and test their code in real-time. Clever AI integration means immediate feedback, so whether you’re refining queries or experimenting with new ideas, this tool enhances productivity by providing swift execution and instant results. Dive into coding with confidence!
Conclusion
‘INTERSECT and EXCEPT in SQL’ are invaluable tools for refining query results. By completing them, you’ll boost your database management skills. Why wait? Dive in and harness the power of SQL today! For more programming insights, explore languages like Java and Python with Newtum. Happy coding!
Download our free SQL Cheat Sheet for quick reference to all operators.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.



