SQL query optimization techniques improve query speed by reducing execution time through indexing, optimized joins, proper filtering, and analyzing execution plans. By applying these methods, you can significantly boost database performance even with large datasets.
As applications scale, slow SQL queries can become a major performance bottleneck. Optimizing queries ensures faster response times, smoother user experience, and reduced server load. Whether you manage enterprise databases or build data-driven apps, mastering SQL optimization is essential today.
Key Takeaways of SQL Query Optimization Techniques
- Use Indexing → Speeds up data retrieval.
- Optimize Joins → Use proper join types and conditions.
- Filter Early → Apply
WHEREandLIMITefficiently. - Check Execution Plans → Identify bottlenecks instantly.
- Avoid SELECT → Select only required columns.
- Use Proper Data Types → Reduces storage and speeds up scans.
- Optimize Subqueries → Convert to JOINs when beneficial.
What Are SQL Query Optimization Techniques?
SQL query optimization techniques are methods used to improve the efficiency and speed of SQL queries. These techniques reduce execution time, lower server load, and ensure faster response for large datasets. They matter because optimized queries enhance application performance, improve user experience, and reduce database costs.

How Does Indexing Improve SQL Query Performance?
Types of Indexes
- B-Tree Index – Default index type; efficient for range searches and sorting.
- Hash Index – Ideal for equality comparisons (e.g.,
WHERE id = 10). - Clustered Index – Stores table data in index order; only one per table.
- Non-clustered Index – Separate structure pointing to table data; multiple allowed.
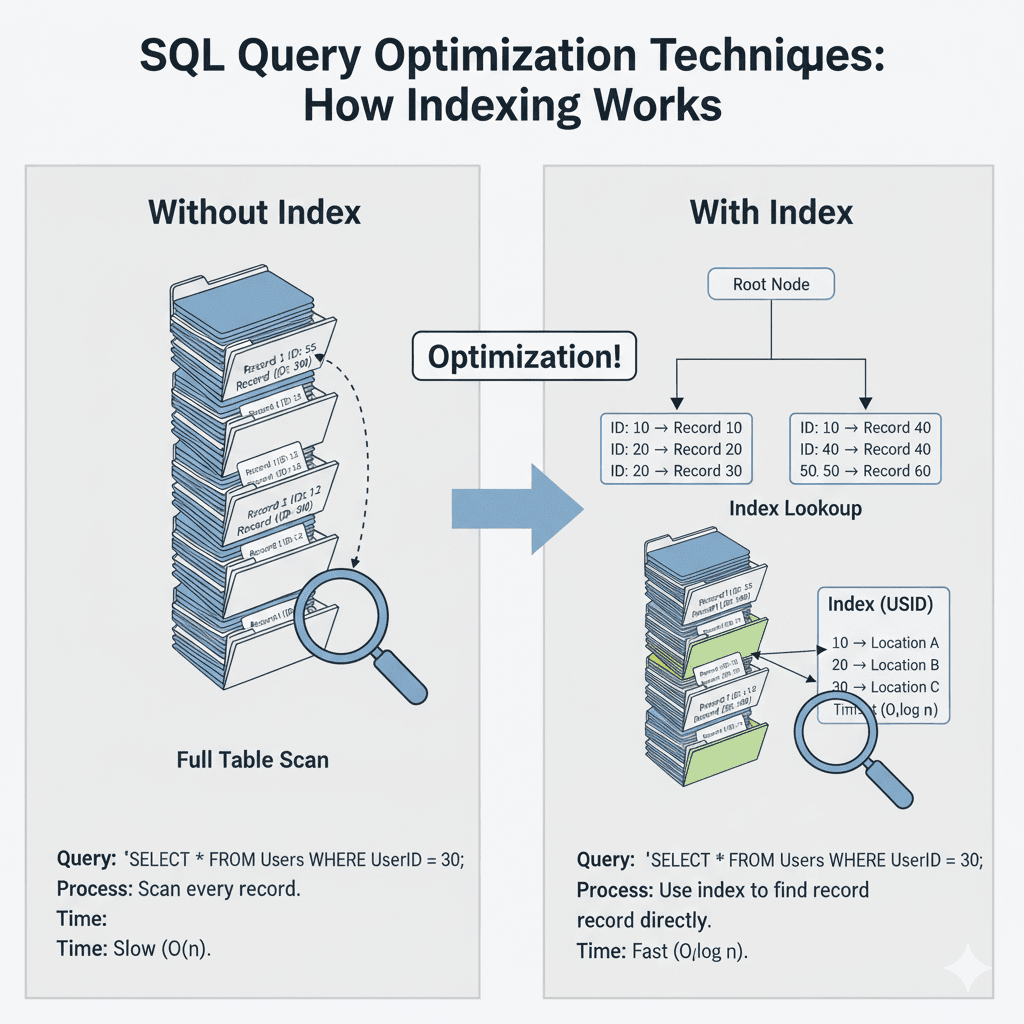
When to Use Indexing
- Use on columns frequently queried with
WHERE,JOIN,ORDER BY,GROUP BY. - Use on high-cardinality columns (e.g., email, user_id).
- Use on foreign keys.
When to Avoid Indexing
- Columns with very low cardinality (e.g., boolean—YES/NO).
- Tables with heavy write operations (indexes slow down INSERT/UPDATE).
- When the index is not used frequently.
Example SQL Snippet
CREATE INDEX idx_customers_email ON customers(email);
Why Should You Avoid SELECT * in SQL?
Impact on Speed
- Causes full table scans.
- Fetches unnecessary data, increasing I/O cost.
- Slows down queries on large tables.
Impact on Memory
- Loads extra columns into RAM.
- Increases network load between database and application.
Better Alternatives
SELECT name, email, created_at FROM customers;
How to Optimize Joins for Faster SQL Queries?
Use Appropriate Join Type
- Prefer INNER JOIN when you only need matching rows.
- Use LEFT JOIN only when necessary.
- Avoid CROSS JOIN unless explicitly required.
Ensure Join Columns Are Indexed
- Always index columns used in JOIN conditions.
- Prevents table scans and boosts join speed.
CREATE INDEX idx_orders_customer_id ON orders(customer_id);
Replace Subqueries With Joins (When Needed)
Slow:
SELECT name FROM customers WHERE id IN (SELECT customer_id FROM orders);
Faster:
SELECT DISTINCT c.name FROM customers c JOIN orders o ON c.id = o.customer_id;
How Do Execution Plans Help in Optimization?
How to View Execution Plans
- MySQL:
EXPLAIN SELECT ... - PostgreSQL:
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT ... - SQL Server: Use Execution Plan button in SSMS.
Common Bottlenecks Identified
- Full table scans
- Missing indexes
- Unnecessary sorting
- Heavy temporary table usage
- Large join buffers
Fixing Table Scan Issues
- Add or refine indexing
- Reduce returned columns
- Apply filters earlier
- Adjust JOIN strategy
Should You Use WHERE, LIMIT, and ORDER BY Carefully?
Best Practices
- Apply the most restrictive condition first.
- Avoid
ORDER BYon unindexed columns. - Use
LIMITfor pagination, not as a performance fix.
SQL Snippets
Slow:
SELECT * FROM orders ORDER BY created_at;
Optimized:
CREATE INDEX idx_orders_created ON orders(created_at); SELECT id, amount FROM orders ORDER BY created_at;
Example: Slow vs Optimized Query
Slow:
SELECT * FROM transactions WHERE status='SUCCESS';
Optimized:
CREATE INDEX idx_transactions_status ON transactions(status); SELECT id, amount, created_at FROM transactions WHERE status='SUCCESS';
How Do Proper Data Types Improve Query Speed?
CHAR vs VARCHAR
- CHAR → Fixed length, faster for uniform data (e.g., country codes).
- VARCHAR → Variable length, saves space for uneven data.
INT vs BIGINT
- Use INT when values fit within range.
- BIGINT consumes more space and slows scans.
Date vs String for Timestamps
- Use
DATE,DATETIME, orTIMESTAMP. - Faster comparisons and sorting than strings.
Common Mistakes That Slow Down SQL Queries
Unnecessary Sorting
- Avoid
ORDER BYwithout a real need. - Always index columns used for sorting.
Excessive OR Operations
- Replace with
INwhere possible. - OR conditions prevent index use in many databases.
Not Using Caching
- Query caching or result caching reduces repeated load.
- Popular in MySQL, PostgreSQL extensions, and Redis-based systems.
Over-indexing Tables
- Too many indexes slow down write operations.
- Review unused indexes and remove them.
Pros & Cons: SQL Query Optimization Techniques
Table Example: Indexing vs No Indexing
| Technique | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Indexing | Faster reads, efficient lookups | Slower writes, storage cost |
| No Indexing | Faster inserts, minimal space | Slow queries, full table scans |
SQL Query Optimization Techniques for Real-world Applications
- Amazon’s Product Recommendations
Amazon uses SQL query optimization techniques to power its product recommendation engine. It optimizes large datasets to ensure quick retrieval of relevant products for users. The company employs indexing and query recompilation to speed up search results and predictions.
By optimizing this query, Amazon reduces the load time for showing top recommended products, enhancing user experience.SELECT product_name
FROM products
WHERE category_id = ?
ORDER BY recommendation_score DESC LIMIT 10; - Spotify’s Playlist Generation
Spotify harnesses SQL optimization techniques to generate and manage playlists. It utilizes sub-queries and efficient filtering to streamline the playlist generation process. This means users get quicker access to curated music lists.
Sub-query optimization allows Spotify to swiftly pull mood-based songs from a user’s preferred genres, leading to a seamless playlist creation experience.SELECT song_id, song_title
FROM songs
WHERE genre_id IN (SELECT genre_id
FROM user_preferred_genres
WHERE user_id = ?)
AND mood = ?; - Facebook’s Friend Suggestions
Facebook optimizes its SQL queries to offer accurate friend suggestions. It involves query refactoring and hints to manage massive datasets efficiently, offering users quick and relevant suggestions.
Optimized queries here make it easier for users to find potential friends based on mutual connections, maintaining high engagement levels.SELECT user_id, friend_id
FROM friends
WHERE user_id = ?
AND mutual_friends > 5
ORDER BY connection_strength DESC;
SQL Interview Questions
- How can joining tables affect query performance in SQL?
Joining tables can significantly impact query performance due to the sheer size of the data being processed. Optimal use of indexes and avoiding unnecessary columns in your SELECT statement can help improve performance. Additionally, understanding the difference between inner and outer joins and using them efficiently can greatly enhance query speed. - What role does indexing play in SQL query optimization?
Indexing is like a map for your database, making it faster to look up data. Without indexes, the database has to scan every row to find the relevant data. Use indexing wisely, as over-indexing can lead to slower write operations. - Are there any strategies for optimizing subqueries in SQL?
One effective strategy is to use joins instead of subqueries when possible. Joins operate on sets of data rather than individual rows, often resulting in faster execution. Also, try to limit the number of subqueries to avoid complex nested operations which can slow down performance. - Why does using the ‘LIKE’ operator sometimes slow down SQL queries?
Using ‘LIKE’ with wildcards at the beginning of a string prevents the use of indexes, forcing a full table scan. Instead, use structured data comparisons or specific string functions if you know the pattern beforehand. - How does data denormalization aid in query performance?
Denormalization eliminates the need for joins by storing related data together, reducing read times at the cost of data redundancy. It’s a trade-off used in situations where read performance is more critical than write efficiency. - Is there any software to help optimize SQL queries?
Many database management systems offer built-in tools for query optimization, such as the Query Analyzer in SQL Server. Additionally, third-party tools like SQL Optimizer or even open-source options can provide valuable insights into query performance and suggest improvements. - What is the impact of using ‘DISTINCT’ on query performance?
‘DISTINCT’ removes duplicate records by sorting, which can be costly in terms of performance, especially on large datasets. Aim to eliminate duplicates from the data source or index rather than in retrieval. - Can partitioning tables enhance SQL query performance?
Yes, partitioning can improve performance by allowing queries to scan only the necessary subset of data. It is particularly effective for queries involving large datasets with a clear logical segmentation. - How should one prioritize optimizing SQL queries?
Start with the queries that consume the most resources, have the longest response times, or are executed frequently. Profiling these queries to identify bottlenecks is an effective starting point. - What are some common oversights when optimizing SQL queries?
A common oversight is ignoring query execution plans, which can reveal inefficient operations. Another is failing to regularly update statistics, which can lead to poor optimization decisions by the SQL engine.
Our AI-powered SQL online compiler lets you instantly write, run, and test your code like a pro! No more endless debugging; with AI assistance, coding becomes a breeze. Watch your skills improve as you learn in real time with this intuitive tool at your fingertips.
Conclusion
“SQL Query Optimization Techniques” enhances database performance and efficiency. Mastering these will empower you to handle complex databases seamlessly. Ready to dive deeper? Achieve more with coding by exploring languages on Newtum today! Start your journey to becoming a proficient programmer.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.



