In C++, arrays are fixed-size collections of elements of the same data type stored in contiguous memory. You can declare an array using syntax like int numbers[5];. Arrays help store and manage multiple values efficiently using a single variable name.
Arrays are fundamental in C++ programming because they allow developers to handle large sets of data efficiently. Whether you’re developing a game, managing database records, or processing large datasets, arrays provide a structured way to store and access data quickly. Understanding their syntax and usage is crucial for writing clean and optimized code.
Key Takeaways about C++ Arrays
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| Syntax | dataType arrayName[arraySize]; |
| Accessing Elements | Use index positions starting from 0 |
| Initialization | int arr[3] = {1, 2, 3}; |
| Fixed Size | Size must be known at compile time |
| Use Case | Storing a list of values of same data type |
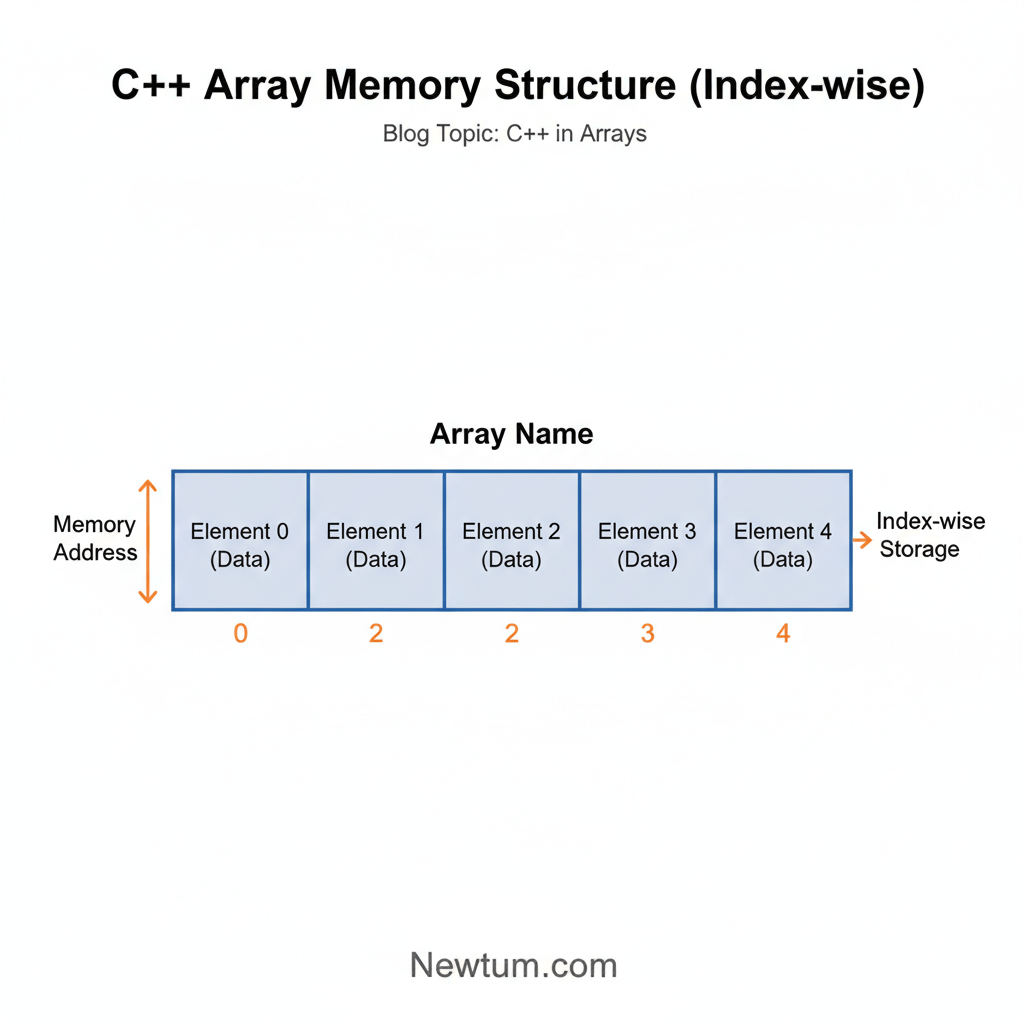
What Is an Array in C++?
An array in C++ is a data structure used to store multiple elements of the same data type in contiguous memory locations. Each element is accessed using its index number, starting from 0. Arrays are useful for managing large datasets efficiently without creating separate variables for each value.
How to Declare an Array in C++
The general syntax for declaring an array in C++ is:
dataType arrayName[arraySize];
Example:
int marks[5];
Here, marks is an integer array that can store 5 integer values. The size (5) must be known at compile time, and all elements belong to the same data type.
How to Initialize and Access Elements in C++ Arrays
Arrays can be initialized during declaration or later in the program.
Example (Initialization during declaration):
int marks[5] = {90, 85, 88, 92, 75};
Example (Accessing elements):
cout << marks[0]; // Outputs 90
In this example, marks[0] accesses the first element of the array.
Types of Arrays in C++
1. One-Dimensional Arrays
A one-dimensional array is a simple list of elements arranged in a single row.
Example:
int numbers[4] = {10, 20, 30, 40};
2. Multi-Dimensional Arrays
A multi-dimensional array, like a 2D array, stores data in a matrix or grid format. It’s useful for applications such as mathematical computations or representing tables.
Example (2D Array):
int matrix[2][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{4, 5, 6}
};
Here, matrix is a 2×3 array, storing values in two rows and three columns.
Sample Code of Working with C++ Arrays
cpp
#include
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Declare an array of five integers
int numbers[5] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// Access and print each element using a loop
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
cout << "Element at index " << i << ": " << numbers[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Explanation of the Code
This simple C++ program showcases how to work with arrays and loops. Here’s a breakdown of what each part of the code does:
- This line, `#include `, is used to include the standard input-output stream, allowing us to use `cout` and `cin` for displaying and capturing input/output.
- The `using namespace std;` line eliminates the need to write `std::` before every standard function like `cout`, making the code cleaner.
- Inside the `main` function, the array `numbers` is declared with a specified size of 5, and initialised with the values `{10, 20, 30, 40, 50}`. This array can store integer values which are accessed by their indices, starting from 0.
- The `for` loop iterates over the array from index 0 to 4, and during each iteration, `cout` prints the value of the array at the current index `i`, illustrating how to access and manipulate array elements in C++.
Output
Element at index 0: 10
Element at index 1: 20
Element at index 2: 30
Element at index 3: 40
Element at index 4: 50
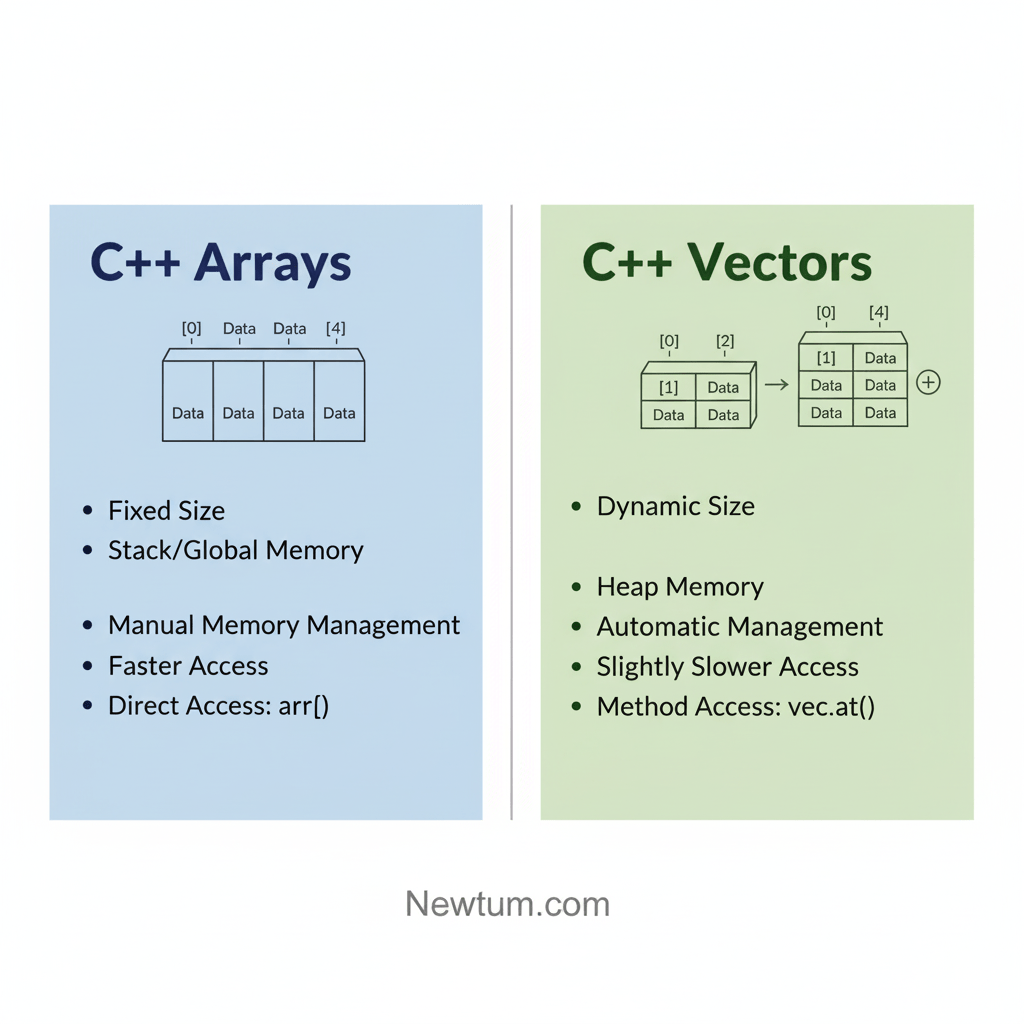
Pros & Cons of C++ Arrays
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Fast data access using index | Fixed size (cannot resize dynamically) |
| Simple syntax and structure | Limited flexibility compared to vectors |
| Efficient memory layout | No built-in boundary checks |
Real-Life Applications of C++ Arrays
- Google: Handling Large Datasets
Google uses C++ arrays to efficiently manage and process vast datasets. These arrays allow quick access to millions of data points, essential for real-time data processing. By storing data sequentially, Google can perform rapid calculations for search algorithms.#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int dataPoints[] = {120, 203, 340, 455, 678};
int total = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
total += dataPoints[i];
}
cout << "Total: " << total;
return 0;
}
Output: Total: 1796 - Microsoft: Memory Management in Operating Systems
At Microsoft, C++ arrays are utilised within the Windows operating system to manage memory allocations efficiently. Using arrays helps segregate processes and allocate space according to each program’s need, enhancing system stability and performance.
Output: Segment: A#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char memorySegments[3] = {'A', 'B', 'C'};
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
cout << "Segment: " << memorySegments[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Segment: B
Segment: C - Amazon: Efficient Product Inventory System
Amazon leverages C++ arrays to maintain and update their massive product inventory systems. Arrays help store and retrieve item details quickly, ensuring up-to-date and accurate availability information for customers.#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string products[] = {"Laptop", "Phone", "Tablet"};
for(int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
cout << "Product: " << products[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output: Product: Laptop
Product: Phone
Product: Tablet
Mastering C++ Arrays
Understanding C++ Arrays can feel daunting at first, but with the right queries, you’ll get the hang of it in no time. Below are some common questions developers are curious about when diving into C++ Arrays. These aren’t the typical ones you find everywhere – they’re unique and might just cover that gap you’ve been wondering about.
- How can you find the size of a dynamically allocated array in C++?
Unfortunately, C++ doesn’t provide a direct function to get the size of a dynamically allocated array. You’ll need to store the size separately when creating the array. - What is the difference between arr[i] and *(arr + i) in the context of arrays?
Both are essentially the same. The expression arr[i] is syntactic sugar for *(arr + i), where you use pointer arithmetic to calculate the value. - Can arrays in C++ be resized at runtime?
No, standard arrays cannot be resized. Instead, you can use vector from the Standard Template Library (STL) which allows dynamic resizing. - How do you pass an array to a function without defining its size?
You can use a pointer to pass the array to a function. Here’s an example:void printArray(int *array, int size) { /* code here */ } - Why does sizeof(arr) return unexpected results when passing an array to a function?
When passed to a function, arrays degrade into pointers, and sizeof returns the size of the pointer, not the entire array. - What’s the difference between multidimensional arrays and arrays of pointers?
Multidimensional arrays are fixed in size for each dimension, whereas arrays of pointers can have varying sizes at each level. - How does one iterate over a C++ array using range-based for loops?
Here’s a simple example:for (int &x : arr) { /* use x here */ } - Can C++ arrays be initialized with non-static data members?
No, you can only initialize arrays with static constants or literal values. - How does an array of chars differ from a string in C++?
An array of chars doesn’t have the same functionalities as std::string, which is a class with useful methods like finding substrings and concatenation. - What’s the best way to manage memory for arrays in C++?
Use smart pointers or STL containers like std::vector to avoid manual memory management, which can be error-prone
Our AI-powered cpp online compiler lets users instantly write, run, and test code. It’s incredibly user-friendly, making it perfect for quick coding sessions. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced coder, the AI assists in enhancing your skills conveniently and effectively. Try it today!
Conclusion
C++ Arrays offer the building blocks for efficient data management in programming. Mastering them enhances your coding prowess, providing a solid foundation for more complex concepts. Give it a shot, and relish the satisfaction of accomplishment. For more insights, explore programming languages like Java, Python, and more at Newtum.
Want to explore more data structures in C++?
👉 Download our free C++ Syntax Reference PDF for quick learning.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.



