Form handling in PHP is the process of collecting, validating, and processing user input submitted through HTML forms using GET or POST methods. PHP allows developers to securely access form data, validate inputs, and store or display results dynamically.
User input powers almost every web application—from login pages to payment forms. Understanding PHP form handling is essential for building secure, interactive, and data-driven websites, especially as backend validation becomes critical for modern security standards.
Key Takeaways of php Form Handling
- GET Method → Sends data via URL, suitable for search forms
- POST Method → Securely sends data in request body
- Validation → Prevents incorrect or malicious inputs
- Sanitization → Protects against XSS and SQL injection
- PHP Superglobals →
$_GET,$_POST,$_REQUEST
What is form handling in PHP?
Form handling in PHP is the process of receiving, processing, and responding to data submitted by users through HTML forms. When a user submits a form, PHP captures the input on the server, applies validation or logic, and then performs actions like saving data, sending emails, or displaying results.
This makes PHP form handling essential for login systems, contact forms, registrations, and feedback pages.
How does PHP collect form data?
PHP collects form data using superglobal arrays, which are available across all scripts without additional configuration.
The most commonly used superglobals are:
$_GET→ Collects data sent via URL$_POST→ Collects data sent in the request body
Example flow:
HTML form → User submits → PHP script reads values → Processes output.
What is the difference between GET and POST in PHP?
GET Method
- Appends form data to the URL
- Suitable for non-sensitive data
- Limited data length
- Easily bookmarkable
POST Method
- Sends data inside the HTTP request body
- More secure than GET
- Supports large data sizes
- Used for passwords, forms, and payments
Best Practice: Use POST for almost all real-world PHP forms.
How do you validate form input in PHP?
Validation ensures that user input is accurate, complete, and safe before processing. PHP validation typically checks:
- Required fields are not empty
- Email and phone formats are correct
- Input length and character types
Common validation techniques include:
- Conditional statements
- Regular expressions (regex)
- Built-in PHP functions like
filter_var()
Validation helps prevent incorrect data and improves application reliability.
How do you secure PHP forms?
Securing PHP forms is critical to protect applications from attacks and data leaks. Key security measures include:
- Sanitizing input to remove harmful characters
- Escaping output to prevent script injection
- Using CSRF tokens to stop fake submissions
- Validating server-side only (never trust client input)
Proper security ensures protection against:
- XSS (Cross-Site Scripting)
- CSRF (Cross-Site Request Forgery)
- SQL Injection
GET vs POST in PHP Form Handling
| Feature | GET | POST |
|---|---|---|
| Data Visibility | Visible in URL | Hidden |
| Security | Low | High |
| Data Limit | Limited | Large |
| Best Use Case | Search forms | Login, payment forms |
Common PHP Form Handling Mistakes (and How to Fix Them)
Even experienced developers make mistakes when working with PHP forms. These issues usually don’t appear during development—but cause bugs, security risks, or data loss in production. Below are the most common PHP form handling mistakes and how to avoid them.
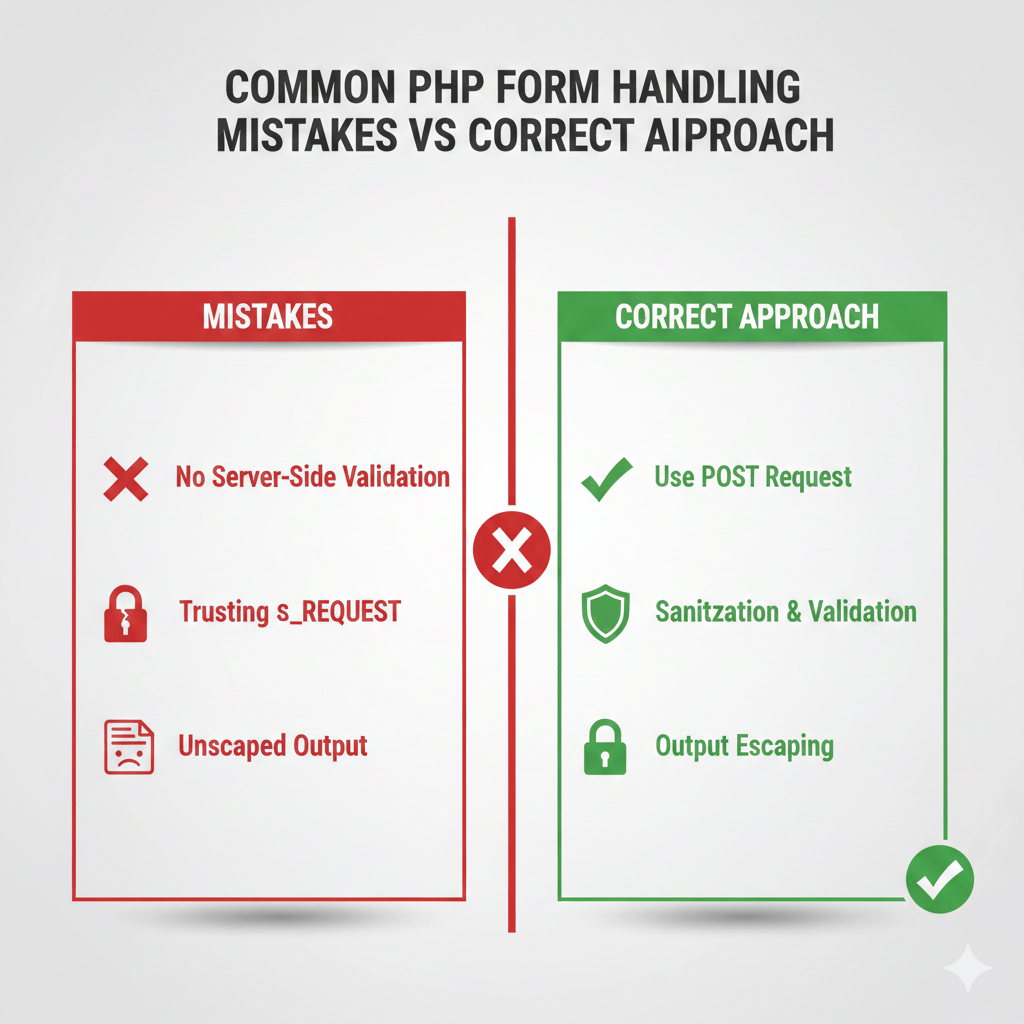
Submitting Forms Without Server-Side Validation
- What goes wrong:
Forms accept any data submitted by the user, including empty fields, incorrect formats, or manipulated values. - Why it’s dangerous:
Client-side validation can be bypassed easily. Without server-side checks, invalid or malicious data reaches your application logic or database. - Correct approach:
Always validate inputs on the server using PHP before processing or storing data. Treat every incoming request as untrusted.
Trusting $_REQUEST Instead of $_POST
- What goes wrong:
Developers use$_REQUESTto access form data without realizing it merges GET, POST, and COOKIE inputs. - Why it’s dangerous:
This makes it unclear where the data came from and opens the door to parameter manipulation or unexpected overrides. - Correct approach:
Use$_POSTfor form submissions and$_GETonly for URL-based data. Be explicit about your data source.
Not Handling Empty or Missing Inputs
- What goes wrong:
The application assumes all fields exist and contain values, leading to warnings, broken logic, or incorrect output. - Why it’s dangerous:
Missing inputs can cause application crashes or allow attackers to exploit unhandled edge cases. - Correct approach:
Always check whether inputs are set and non-empty before using them. Gracefully handle missing data with user-friendly messages.
Forgetting to Escape Output
- What goes wrong:
User-submitted data is displayed directly on the page without escaping. - Why it’s dangerous:
This exposes your application to Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks, where attackers inject malicious scripts. - Correct approach:
Escape all output before rendering it in HTML, even if the data was previously validated or sanitized.
Relying Only on JavaScript Validation
- What goes wrong:
Forms rely entirely on client-side validation and assume users cannot bypass it. - Why it’s dangerous:
JavaScript can be disabled, modified, or skipped entirely. Attackers can submit invalid data directly to your PHP endpoint. - Correct approach:
Use JavaScript only for user experience improvements. PHP must always perform the final validation and security checks.
Real-World PHP Form Handling Workflow (End-to-End)
In real applications, PHP form handling is not just about collecting input—it’s about validating, securing, processing, and responding reliably. The workflow below reflects how production-ready PHP applications actually handle forms.

1. User Fills the Form
The user interacts with an HTML form such as a contact form, login form, or registration form. At this stage:
- Input can be incomplete or incorrect
- Data may be intentionally manipulated
- No assumptions should be made about accuracy
In real projects, every form submission is treated as untrusted input.
2. Client-Side Validation (Optional but Recommended)
Client-side validation improves user experience by:
- Catching obvious errors early
- Reducing unnecessary server requests
- Providing instant feedback
However, this step is never trusted in isolation because it can be bypassed.
Purpose: UX improvement, not security.
3. Server-Side Validation (Mandatory)
This is the most critical step in PHP form handling.
At this stage, PHP:
- Confirms required fields are present
- Validates data formats (email, numbers, text length)
- Rejects invalid or incomplete submissions
Without server-side validation, the application is insecure by default.
4. Sanitization
After validation, input data is cleaned to remove harmful or unexpected characters.
Sanitization helps:
- Prevent XSS attacks
- Protect databases and logs
- Ensure consistent data storage
This step prepares the data for safe usage in output, emails, or databases.
5. Business Logic Execution
Once data is validated and sanitized, PHP performs the intended action, such as:
- Saving data to a database
- Sending an email notification
- Triggering account creation
- Logging user activity
This is where the actual purpose of the form is fulfilled.
6. Success or Error Response
Finally, PHP sends a response back to the user:
- Success message (form submitted successfully)
- Validation errors (with helpful feedback)
- System errors (handled gracefully)
In real projects, error messages are:
- User-friendly
- Non-technical
- Free of sensitive information.
PHP Form Handling Checklist Before Going Live
Before deploying any PHP form to production, use this checklist to prevent common bugs, security issues, and user complaints. This checklist reflects how professional teams review forms before release.

Validation & Security
- All required fields are validated on the server
- POST method is used for form submission
- Inputs are sanitized before processing
- Output is escaped before rendering
- CSRF token is implemented and verified
Data Handling
- No sensitive data appears in the URL
- Form data is processed only once per submission
- Duplicate submissions are handled or prevented
- Error handling does not expose system details
User Experience
- Error messages are clear and user-friendly
- Form retains user input on validation failure
- Success messages confirm next steps
Performance & Reliability
- Form works with JavaScript disabled
- Large inputs are handled gracefully
- Timeouts and limits are considered
How PHP Form Handling Breaks in Production (and Why)
Most PHP forms work perfectly in local development—but fail unexpectedly in production. Below are real-world reasons why.
Missing Server Configuration
- What happens:
Forms fail silently or return unexpected errors. - Why:
Production servers may have different PHP versions, disabled extensions, or stricter error settings. - Impact:
Forms stop processing without clear feedback.
File Upload Limits
- What happens:
File uploads fail even though the form appears correct. - Why:
Server limits such asupload_max_filesizeandpost_max_sizerestrict file handling. - Impact:
Users see broken uploads without explanation.
Incorrect Form Encoding
- What happens:
File data or special characters are missing. - Why:
The form encoding type is not set correctly. - Impact:
Data is partially received or completely lost.
Session Timeout Issues
- What happens:
Users submit a form and receive authentication or token errors. - Why:
Sessions expire before submission, especially on long forms. - Impact:
Valid submissions are rejected.
Hosting Environment Differences
- What happens:
Forms behave differently across hosting providers. - Why:
Differences in PHP versions, security rules, or server modules. - Impact:
Forms that worked locally fail in production.
PHP Form Handling in Real-Life Applications
- Facebook: User Registration Form
PHP Form Handling is crucial for social media platforms like Facebook during user registration. It captures user input, validates it, and stores it securely in a database.
This code snippet ensures input data is only processed after being submitted via POST, enhancing security. Facebook can manage millions of user registrations smoothly by employing such techniques.if ($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST") {
$username = $_POST["username"];
$email = $_POST["email"];
// Perform validation and store in database
} - Amazon: Checkout Process
E-commerce giants like Amazon utilise PHP Form Handling in their checkout-processing forms to capture user details and payment information securely.
This captures billing and payment data effectively, ensuring the checkout process is seamless and secure for millions of customers.if (isset($_POST['checkout'])) {
$billing = $_POST['billing_address'];
$paymentMethod = $_POST['payment_method'];
// Authenticate and proceed with payment
} - LinkedIn: Job Application Forms
LinkedIn uses PHP Form Handling to collect and process data from job application forms, making job tracking efficient for recruiters and applicants.
Streamlined data collection empowers LinkedIn to handle thousands of job applications daily, providing a better user experience.if ($_POST['submit']) {
$jobID = $_POST['job_id'];
$applicantName = $_POST['name'];
// Save application data
}
FAQ: PHP Form Handling
1. Is PHP form handling secure by default?
No. PHP does not automatically secure form data. Developers must apply proper server-side validation, input sanitization, and output escaping to protect against XSS, CSRF, and SQL injection attacks.
2. Can PHP handle multiple form inputs at once?
Yes. PHP can process multiple form fields simultaneously using associative arrays such as $_POST or $_GET, making it easy to manage complex forms with many inputs.
3. Why is POST preferred over GET for forms?
POST is preferred because it sends data in the request body instead of the URL, offering better security, support for larger data sizes, and safer handling of sensitive information.
4. Do I need JavaScript if I use PHP form handling?
No. PHP alone can fully handle form processing and validation. However, JavaScript enhances user experience by providing instant client-side validation before submission.
Our AI-powered php online compiler offers a seamless coding experience. Instantly write, run, and test your ‘php’ code with the help of AI. It’s designed to streamline your coding process, making it quicker and more efficient. Try it out, and see the difference AI can make!
Conclusion
Mastering ‘php Form Handling’ equips you with the skills to manage user input efficiently, creating dynamic web pages that interact seamlessly with databases. Give it a try to experience the satisfaction of building something functional! For more programming adventures in languages like Java, Python, C, and C++, visit Newtum.
Edited and Compiled by
This article was compiled and edited by @rasikadeshpande, who has over 4 years of experience in writing. She’s passionate about helping beginners understand technical topics in a more interactive way.



